Intelligent Agents and Multi-Agent Collaboration: Advancing Networks to New Heights of L4 Autonomy
The "AI+" initiative has been included in China’s government work report for two consecutive years, with the 2025 report specifically advocating for the widespread application of large models. To drive AI technology towards commercial success, it is crucial to implement technology in practical scenarios and iterate cognitive paradigms. AI agents serve as the bridge between AI technology and its commercial application. In 2025, AI agents and multi-agent collaboration technologies are rapidly evolving, driven by both research and applications.
In network operation and maintenance, AI agents can unify the scheduling of large and small models alongside various network management system capabilities, creating a new paradigm for network O&M. TM Forum's "Autonomous Network: L4 Industry Blueprint—High-Value Scenarios", released in November 2024, introduces full-stack AI, updates the system architecture, and incorporates AI agents into the resource operation, business operation and commercial operation layers. The adoption of single-agent tools, together with cross-layer and cross-domain collaboration among multiple AI agents, will be key to driving the incremental evolution of autonomous networks towards L4 autonomy by 2030.
Empowering L4 High-Value Scenarios with Agents and Multi-Agent Collaboration
Building on TM Forum's high-value scenarios, ZTE has expanded its scope by identifying approximately 30 high-value scenarios for L4 advanced autonomous networks. These include handling personal service complaints, optimizing the quality of 5G private networks and IoT services, monitoring and handling network failures, and improving network performance.
To address these high-value scenarios, ZTE is focusing on developing six types of assistants and seven types of expert agents based on the Nebula Telecom Large Model and Nebula Telecom Specialized Models (such as the Signaling Large Model and Spatio-Temporal Large Model) (see Fig. 1).
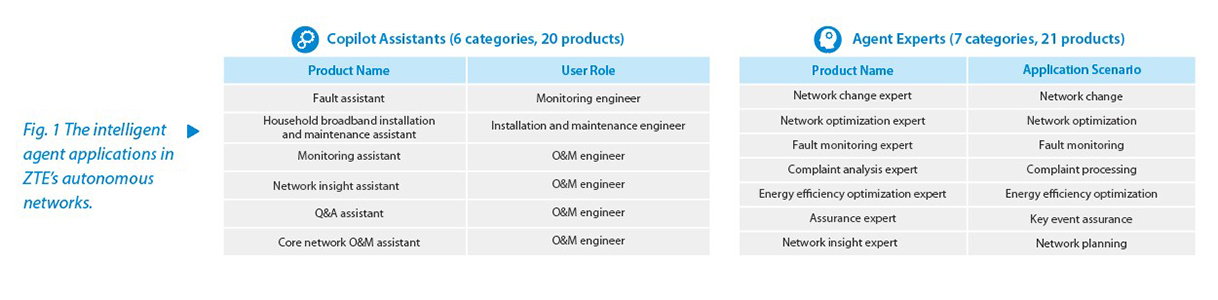 Leveraging intelligent agents and multi-agent collaboration, ZTE has established several high-level autonomous network practices, including intelligent handling of network cloud failures, mobile network service complaints, and cross-domain failures.
Leveraging intelligent agents and multi-agent collaboration, ZTE has established several high-level autonomous network practices, including intelligent handling of network cloud failures, mobile network service complaints, and cross-domain failures.
Network Cloud Fault Intelligent Handling
Built on ZTE's cloud infrastructure intelligent analysis system (CIIA), the network cloud fault handling application utilizes multi-agent technology to dynamically decompose over 70 task with an accuracy rate of over 90%. This approach effectively handles complex domain tasks and and has been verified in the field. In practical applications, a telecom operator deployed the CIIA product, leveraging the Log Large Model's fault monitoring and diagnosis capabilities to enhance automation in on-site fault handling, reduce reliance on experts, and significantly save on workload. The process of identifying and diagnosing switch faults was reduced from over 140 minutes to less than 20 minutes.
Intelligent Handling of Mobile Network Service Complaints
ZTE's VMAX mobile service complaint solution introduces a complaint analysis agent that helps operators improve the quality and efficiency of complaint handling across four key stages: complaint reception, preliminary processing, complaint resolution, and quality control archiving. Compared to traditional methods, automated analysis significantly reduces the number of complaint tickets and shortens response times. As a result, the overall handling time for mobile service complaints is reduced by 50%, the interception rate for network issue complaints increases by 20%, fault localization accuracy reaches 84%, and first-line maintenance dispatching time is cut by 10%.
Intelligent Cross-domain Fault Handling
ZTE's fault monitoring expert, through the coordinated operation of a cross-domain analysis agent, a single-domain analysis agent, and a solution generation agent, seamlessly integrates fault identification, demarcation, localization, and scheduling execution. It also enables high-level collaborative analysis between the business layer and the network layer at both cross-domain and single-domain levels. In practical applications, a provincial mobile operator improved the IP network fault monitoring process with significant results: fault identification time was reduced from 5 minutes to real-time level of 1 minute, average repair time (MTTR) decreased by 8%, and the accuracy of fault demarcation by the large model significantly increased by 20%, reaching 91%.
Advancing Continuously to Tackle Challenges in Advanced Autonomy
L4 autonomy requires multi-agent collaboration across layers and domains to achieve end-to-end closed loops in complex scenarios, ultimately enabling distributed decision-making along with high-level flexibility and high-level scalability. Despite continuous advancements, challenges remain in multi-agent collaboration technology, the effectiveness of embedding applications into production, and the development of an ecosystem with protocols and platforms.
From a technological perspective, the multi-agent collaboration framework is still under development. Issues persist, such as the amplification of hallucinations among agents and the insufficient validation of decentralized communication mechanisms in applications. ZTE's Nebula AI Agent Engine supports cooperative, competitive, and mixed collaboration types, as well as rule-driven, role-driven, and model-driven collaboration strategies to pragmatically address these challenges step by step.
In terms of application, ZTE achieved significant verification results in 2024 in high-value scenarios such as energy conservation, cross-domain fault analysis, and network changes. These were set as benchmarks and replicated at scale. In 2025, ZTE will enhance value-effectiveness verification for key high-value scenarios, such as wireless network optimization and fault management in autonomous networks, embedding them into production processes and collaborating with partners to facilitate replication.
From an ecological perspective, although protocols and platforms related to AI agents are constantly emerging, the lack of unified standard poses a challenge to interoperability. ZTE continues to embrace open-source ecosystems and contribute to open-source communities to accelerate the maturity of open-source standards. In April 2025, during authoritative GAIA benchmark tests, ZTE open-sourced the Co-Sight Super AI Agent and topped the open-source framework list with an average score of 72.72. Meanwhile, the Nebula Agent Engine supports open-source protocols such as the model context protocol (MCP).
Looking ahead, ZTE will join hands with industry partners to build a comprehensive ecosystem for large models and AI agents. By overcoming technical barriers and enriching agent-centric high-value scenario applications for end-to-end autonomous networks, ZTE aims to advance networks to new levels of autonomy.