Intelligent Agent Factory: Agile Way to Industrial-Grade Agents
When Manus gained global attention as the first universal agent, agent technology was undergoing a critical transition from laboratory research to industrial-scale production. To tackle three major pain points of traditional agents—long development cycles, inconsistent quality standards, and low asset reusability—the Intelligent Agent Factory was introduced. ZTE has developed the industry's first industrial-grade AI Agent platform that implements a "production-evaluation-optimization-closed-loop" workflow, driving agent development into the industrial era through standardized, modular production.
Core Architecture and Production Model of Agent Factory
The industrial-grade AI Agent Factory is based on a cloud-native architecture with underlying support for heterogeneous computing such as multi-vendor GPUs and inference cards, providing end-to-end support for the design, development, and operation of large-model-based agent applications (see Fig. 1).
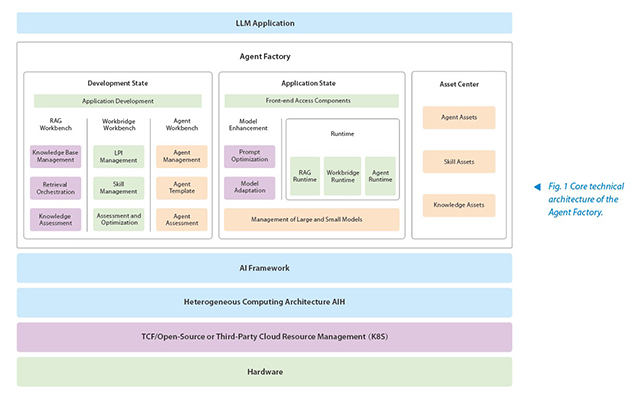
RAG Workbench: Knowledge Assembly Workshop
The RAG workbench helps users quickly build applications powered by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology. It enables effortless construction of knowledge bases through key steps such as corpus upload, intelligent segmentation, and embedding model selection, while also supporting evaluation and optimization with test datasets. Its knowledge retrieval feature provides customizable workflows, allowing flexible adjustments to retrieval strategies to enhance the response quality of RAG systems. With the RAG workbench, users can achieve end-to-end knowledge management and performance evaluation, rapidly developing high-accuracy, high-performance RAG applications.
WorkBridge Workbench: The Intelligent Hub Connecting Natural Language with APIs
WorkBridge is a development tool that bridges atomic capabilities and extends the capabilities of large models. It accurately maps natural language to existing APIs via natural language programming interface (LPI), enabling intelligent invocation—using language as command—to drive API execution. Its core features include:
- LPI management: Supports the creation, optimization, evaluation, and release of LPIs, ensuring accurate and reliable mapping between natural language and APIs.
- Skill management: Combines multiple LPIs into reusable business skills, providing full lifecycle management for these skills.
WorkBridge effectively lowers the technical barriers to development, accelerates intelligent application development, and sets a benchmark for engineering practices in natural language to API (NL2API) technology.
Agent Workbench: The Ultimate Assembly Station for Intelligent Agents
The agent workbench offers three approaches to meet diverse user needs for agent assembly: rapid development based on pre-built templates, AI-assisted intelligent construction, and customized professional development.
During the development process, the workbench provides a visual configuration interface and intelligent conversational assistance, enabling developers to quickly complete core configurations, such as agent role definition, knowledge base association, and tool integration. Developers can validate agent performance through manual testing or automatically generated test sets.
In addition, the workbench provides powerful evaluation and optimization capabilities, offering multi-dimensional metric analysis and comprehensive assessment reports to support continuous refinement. It also leverages AI to generate intelligent optimization suggestions, helping developers rapidly enhance agent performance.
Dual-State Collaboration: An Industrial-Grade Agent Production Pipeline
The dual-state model empowers industrialized agent production: in the "Development State," knowledge production, skill development, and agent assembly are collaboratively completed through three major workbenches (RAG, WorkBridge, and Agent), with the agents entering the asset center after rigorous testing. In the "Application State," the asset center enables one-click deployment, forming a standardized pipeline from raw materials to finished products. This pipeline balances quality and efficiency, providing reliable support for large-scale AI deployment.
In-Depth Practice: Crafting a Network Fault Monitoring Agent
Traditional monitoring systems suffer from delayed fault detection, low accuracy in root cause identification, and inefficient cross-system coordination. These challenges urgently require the application of AI technology to build an intelligent fault monitoring system, enabling a qualitative shift from passive response to proactive prevention.
ZTE adopts a progressive knowledge–skill–agent architecture to create a network fault monitoring expert.
Knowledge Engineering: Building the Intelligent Foundation
In the scenario of network fault monitoring, enabling the system to perform efficient and accurate interactive fault diagnosis requires the establishment of a knowledge system that covers fault definitions across multiple domains and scenario-based handling guidelines. The implementation involves two key aspects:
- Knowledge base construction: Supports importing from text, Word, and PDF files. The focus is on building a fault knowledge base (including fault definition standards, fault handling guidelines, alarm response manuals, etc.) and an equipment information database (mapping relationships between full and abbreviated names of equipment). Document import and intelligent segmentation are completed via the RAG workbench.
- Retrieval mechanism design: Adopts a hybrid vector + keyword retrieval model, utilizing the RAG workbench's visual workflow orchestration capabilities to intelligently re-rank retrieval results.
Capability Assembly: Unblocking the System's Meridians
Monitoring center engineers often need to frequently switch between multiple systems to handle faults. To address this issue, ZTE has encapsulated the APIs of the capability open platform (for retrieving alarms, performance metrics, logs, etc.), the work order platform, and the single-domain workbench (for topology queries) with natural language conversion. Using WorkBridge, APIs are converted into LPIs, and multiple LPIs are combined to form complete skills. Currently, 15 external system APIs have been encapsulated, supporting end-to-end closed-loop fault monitoring and handling.
Agent Production: Building a Digital Expert Team
ZTE has established a specialized "task force" for fault monitoring scenarios, comprising a fault identification agent, a fault analysis agent, a fault dispatch agent, and a report generation agent.
Taking the fault analysis agent as an example, its core function is to achieve fault demarcation and localization through multidimensional data analysis. In actual network operation and maintenance, fault analysis approaches vary across domains. For instance, addressing data network faults requires integrating aspects such as equipment in the computer room and transmission links, while network cloud faults necessitate layer-by-layer analysis from hardware to virtual layers and network elements. We design the demarcation and localization methods as a chain of thought stored in the knowledge base, then configure the agent with this knowledge base and equip it with skills such as alarm analysis and log analysis. After assembly, the agent undergoes iterative testing and optimization. Once it meets the standards, it is released to the asset center and deployed in the production environment.
Implementation Results
At a provincial operation and maintenance center, ZTE's fault monitoring expert "digital employee" operates 24/7, capable of accurately identifying faults within one minute and achieving a 91% accuracy rate in complex fault demarcation. Efforts are underway to vertically expand professional domains and horizontally broaden application areas, continuously enhancing the coverage of intelligent operation and maintenance.
In the future, the AI Agent Factory will evolve along two key directions: automation and specialization. For automation, AI technology will be leveraged to achieve an end-to-end closed-loop process from demand analysis to performance optimization, lowering the development threshold. For specialization, predefined agent template libraries will be constructed based on the communications field, enabling out-of-the-box deployment and accelerating the rollout of intelligent agent applications. As intelligent technologies advance, the AI Agent Factory is set to become the foundation for enterprise intelligent transformation, unlocking the inclusive value of AI.