AI+ Core Network: Towards 6G Evolution
The evolution of the next-generation core network is driven by AI. While the AI architecture shifts from centralized external plug-ins to ubiquitous endogenous integration, AI is driving the network architecture change, evolving the 6G core network from traditional data transmission into the neural center of intelligent services.
AI Architecture Transformation
Fig. 1 shows the endogenous intelligent architecture of the core network. The evolution of the AI architecture is reflected in the following aspects:
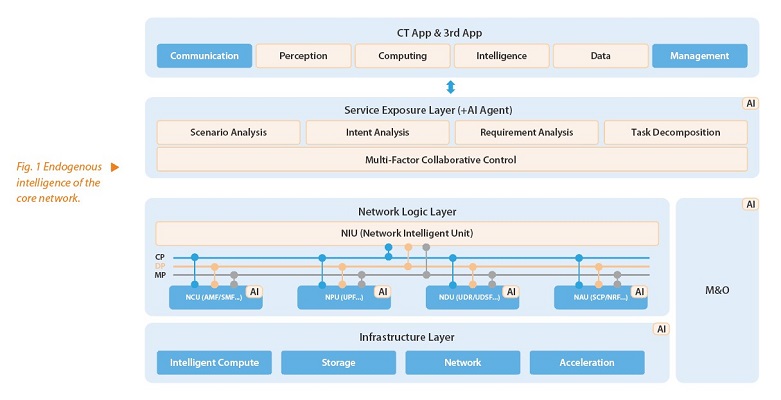
- Centralized to ubiquitous: The system evolves from a centralized AI architecture, centered around the network data analysis function/management data analysis function (NWDAF/MDAF), to a distributed, ubiquitous AI architecture, enabling better adaptation to dynamic user requirements and traffic patterns and the delivery of more flexible and personalized services.
- AI for Network to Network for AI: The evolution is shifting from network intelligence that optimizes network performance, efficiency, and user experience through AI, to AI as a service (AIaaS) that provides end-to-end service guarantee and capability services for AI applications.
- Single-body to multi-body: AI serves as the core to coordinate cross-layer and cross-domain resources, meeting the connectivity, computing, data, and model requirements of various real-time services such as immersive experiences.
- High-order intelligence with AI+ digital twin: The AI agent understands intent and can reflect the real-time behavior and performance of the real physical world through digital twin construction, enabling accurate spatiotemporal inference for the physical world. This is applicable to scenarios such as autonomous driving, robotics, intelligent industrial production, and remote healthcare.
AI Leading Network Architecture Change
To address the challenges of multiple NEs, complicated interaction, and the slow launch of new functions in 5G/5G-A, as well as to meet the future 6G requirements such as immersive communication, endogenous intelligence and integrated sensing and communication, ZTE proposes a unified, intelligent service-based architecture (iSBA) powered by AI and enhanced by dual channels and AI-agent multi-element coordination. Built on iSBA, ZTE has created the intelligent distributed communication network (iDCN) and the AI-agent real-time communication network (ARCN), laying the foundation for the 6G embodied AI core network: AI Core.
Unified Network Architecture Base
iSBA is the cornerstone of the 6G network architecture. While cloudification + SBA/eSBA networks have enabled the success of the 5G/5G-A network architecture, the iSBA introduces new key features such as intelligence, service-based design, and multi-element integration:
- Intelligence (intelligent base): iSBA provides a unified intelligent base encompassing GPU, AI OS, and AI cloud full-stack intelligence. The iDCN and ARCN, built on this base, not only saves software and hardware resources, but also reuses AI’s basic functions and frameworks—facilitating network-service coordination and network-media integration.
- Service-based (high-speed channel): Based on the service-based interface (SBI), SBA/eSBA unifies and simplifies the signaling interaction interface between NEs. The iSBA further introduces a data communication interface (DCI) to establish dual channels together with SBI. SBI and DCI work collaboratively: SBI transfers signaling data, while DCI transfers large data streams, enabling high-performance interaction between NEs. In addition, iSBA integrates and streamlines 5G NEs, proposing an ultra-simple network architecture that supports microservices, plug-ins, agile frameworks, and plug-and-play capabilities.
- Multi-element (integrated scheduling): In the future, evolution will shift from single communication to the integration of multiple elements—including communication, sensing, computing, and intelligence—achieving unified scheduling based on AI agents. The system will leverage AI for multimodal intent identification, decomposes complex tasks, and schedules atomic capabilities across multiple elements, orchestrates resources and procedures, and visualizes resource distribution through digital twins.
Intelligent Distributed Communication Network
During the evolution to 6G, the current network faces many challenges, including increased architectural complexity, limited automation in O&M, and growing security and reliability risks. In the future, the 6G network will need to support more types of users and services. The number and types of terminals as well as the number of subnets will increase exponentially, imposing higher requirements on network performance and service experience. These new service requirements, along with existing network issues, drive the evolution of networks towards iDCN (Fig. 2).
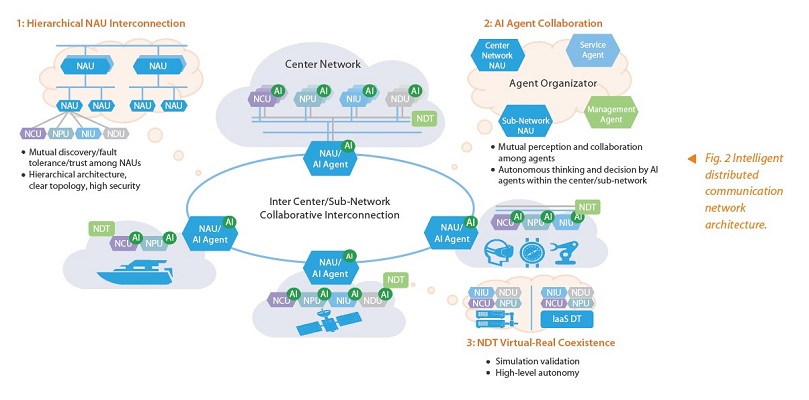
The iDCN network has the following key features:
- Intelligence: Evolves from external AI to internal collaboration to meet the end-to-end intelligent collaboration requirements of future networks and services. Within a domain, centralized management and control are combined with distributed coordination to form hierarchical intelligence and enable autonomous intra-domain networks. Across domains, intelligent coordination is achieved via AI agents.
- Simplicity: Evolves from NE interconnection to subnet interconnection, providing an architecture basis for fast service and network expansion. Within a domain, inter-NE signaling interactions are minimized through the aggregation of information and functions. Between domains, subnet interconnection and discovery replace NE interconnection and discovery, simplifying the topology and procedures for interconnection discovery and selection.
- Flexibility: Evolves from manual configuration to plug-and-play, enabling fast service deployment, dynamic resource sharing, and network automation and intelligence. Within a domain, network functions can be extended through plug-ins, reducing the impact on peripheral NEs and the TTM for new functions and services. Across domains, network-level plug-and-play is enabled through the automatic management mechanism of on-demand subnet creation and deletion.
- Security: Evolves from physical protection to a virtual-physical symbiosis to improve both network security and reliability. Within a domain, the network digital twins (NDT) technology is introduced to enhance user, network, and service state awareness, improving active immunity. Inter-domain isolation protection, topology hiding, and secure access are implemented through the network assisted unit (NAU).
Three key technologies in the iDCN include:
- Hierarchical NAU interconnection: Mutual discovery, disaster recovery, and trust assurance between NAUs replace the existing inter-NE mesh interconnection architecture.
- AI agent coordination: The NAU integrates AI agent capabilities to support autonomous task processing and decision-making, perceive the status and capabilities of each functional service within the domain, and collaborate with other inter-domain network nodes and agent functions to improve the intelligent management and operational optimization capabilities of autonomous networks.
- NDT virtual-real coexistence: By constructing a digital twin system for the core network, real-time perception and predictive analysis capabilities are enabled. Simulation-based verification and virtual-real interaction guarantee the network’s operating system and improve its intelligent autonomy.
Agent Real-Time Communication Network
In the future, real-time communication will evolve from "audio and video" to multimodal communication involving touch, taste, and perception; from "human-object" communication to "human-object-virtual" communication; and from "real body" to "avatar or digital counterpart" communication, enabling real-time communication services for 6G-native intelligent agents. Based on the unified iSBA, the 6G core network integrates the data, media, and intelligent planes of the 6G network and real-time communications, offering a unified, plug-in-based intelligent architecture that supports multimodal communication between agents.
- Intelligence empowering network (AI for ARCN): Through endogenous AI agents, the system provides 6G-native real-time communication services to enable multimodal "human-object-virtual" communication. The AI agent, with LLM/MLLM at its core, performs task decomposition, inference, decision-making, reflection, and self-learning. It uses technologies such as RAG for short- and long-term data storage, inputs data into the LLM/MLLM as context, completes tasks through the tools, and extends real-time communication services from the physical world to the digital world.
- Network empowering intelligence (ARCN for AI): The AI agents will be distributed across terminals, wireless networks, core networks, and even third-party networks. The iSBA dual channels (SBI and DCI) provide efficient transport capacity for coordination between agents, as well as for data and model transmission, thereby enabling high-speed and deterministic real-time communication between AI agents and between AI agents and humans.
Multi-Element Coordination
The 6G network needs to solve the challenge of coordinating diverse resources and capabilities, enabling different services to be scheduled to the optimal compute node via the optimal network path, so as to meet the specific QoS requirements and achieve optimal alignment between requirements and resources.
Multi-element coordination refers to the coordination of computing and network resources under diverse QoS constraints. Elements denote the factors being coordinated, while computing and network resources are the objects of coordination. Key technologies include multi-element identification, multi-element perception, multi-element measurement, multi-element orchestration and scheduling, multi-element QoS, and multi-element coordination capability openness.
Multi-element coordination spans multiple domains, including cloud, edge, terminal, RAN, and core network, and covers multiple dimensions, such as communication, sensing, intelligence, computing, and security. It is challenging to introduce integrated AI agent capabilities to solve the complexity of multi-element coordination, provide differentiated and customized services for users, and achieve optimal matching between requirements and resources at minimum cost.
AI is driving the evolution of networks toward 6G, simplifying the network and making it more flexible and customizable. It will empower 6G to serve all industries and the intelligent world, supporting sustainable and high-speed development of society.