ZENIC ONE: An Intent-Based Intelligent Product
The advent of 5G combined with AI has led to widespread enthusiasm for innovations to improve the productivity of telecom networks and achieve network automation. The concept of intent-based networking (IBN) put forth by Gartner in 2017 is getting a lot of attention in the industry. Standard bodies like 3GPP, ETSI and CCSA have initiated research on IBN. It is gradually becoming clear that the future network should be self-planning, self-adjusting, self-optimizing, self-managing, and allocate on-demand resources so as to align itself with the intent without human involvement.
Based on its deep understanding of network development and rich accumulation in ICT technologies, ZTE launches the ZENIC ONE, an IBN-oriented intelligent product. The product covers the full lifecycle of the network and provides such intelligent services as network planning, rapid network deployment, automatic service provisioning, automatic service recovery, quick fault diagnosis, network simulation, network prediction and network optimization, which effectively reduce network Capex and Opex, improve the level of intelligence as well as the efficiency of network construction and O&M.
Architecture
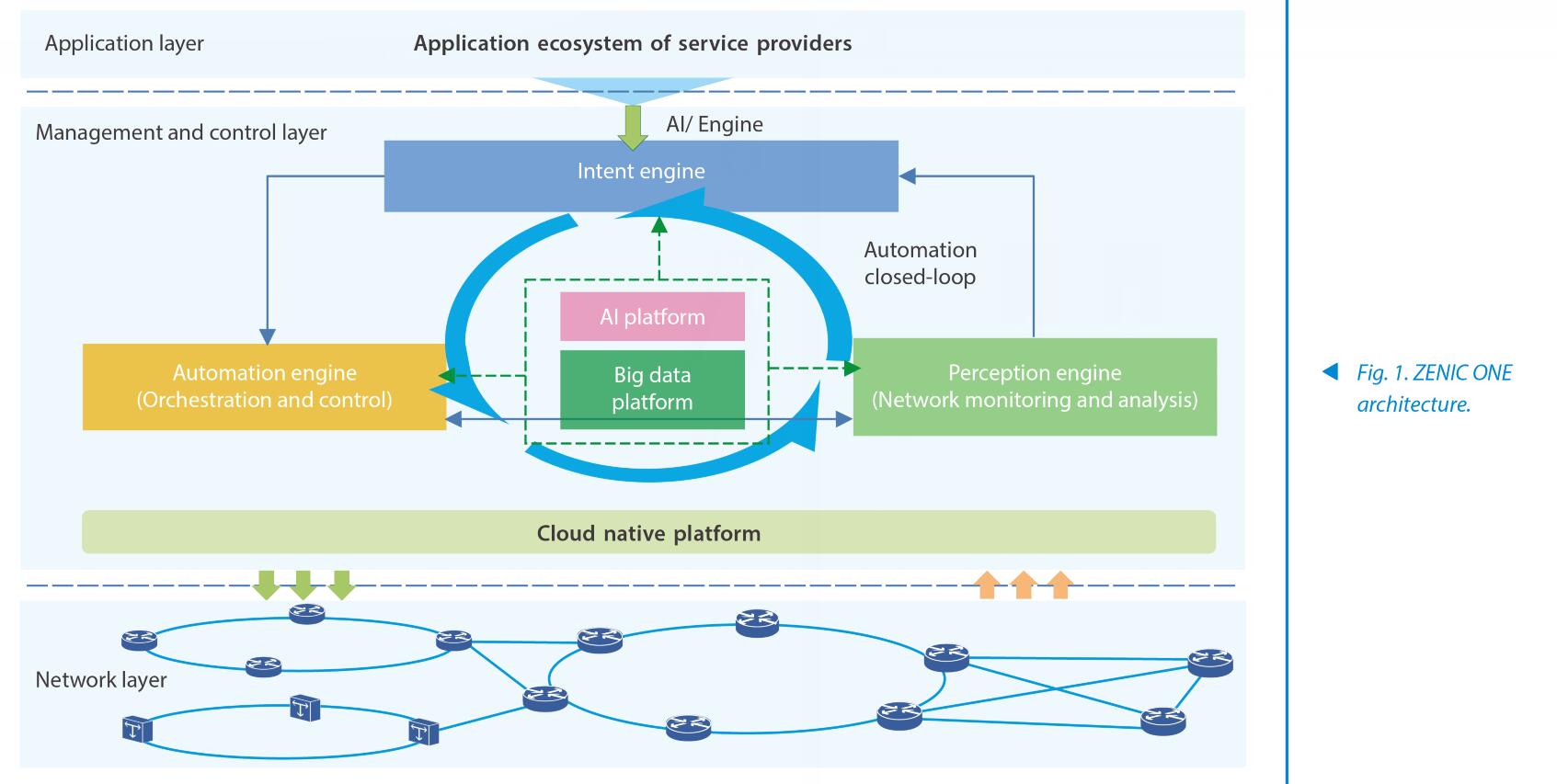
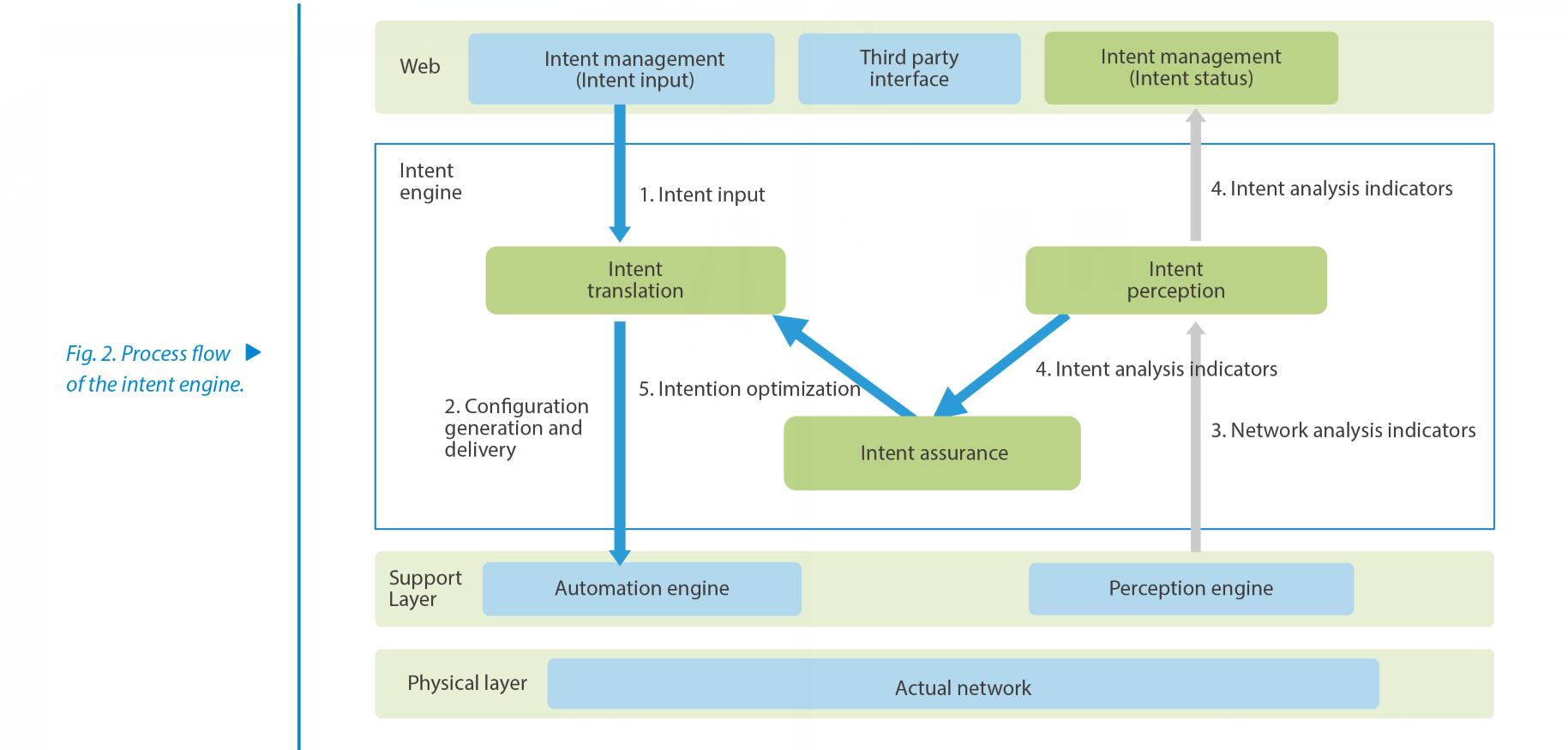
The intent engine includes three components: translation, perception, and assurance (Fig. 2). The intent engine offers a web interface and third-party northbound interfaces. After users express their intents by voice, text or other modes through the web interface, the translation component interacts with them to ensure the integrity and clarity of the intent. The translation component also ensures that intent is implemented consistently. An intent, whether it is user's input or remediation/optimization inside the network, is converted into a unified network intent expression model, goes through the processes of solution design, network orchestration, and pre-verification, and then is translated into configurations and sent to the automation engine. The perception component analyzes the network data reported by the perception engine against the intent, and sends the analysis results to both the management component (intent status) and the assurance component. The assurance component performs bandwidth adjustment, path adjustment, and protection recovery based on set policies to ensure the quality of the user intent.
The perception engine collects and stores massive data in the entire network, and uses machine learning algorithms for association analysis, data mining and prediction, and then sends network analysis results to the perception component in the intent engine.
The third-party northbound service is interconnected with the operator's upper-layer system, and they together implement automatic provisioning of services. It supports smooth evolution of the operator and rapidly meets new service requirements.
Features
The ZENIC ONE is an open, intelligent system with the following features:
—Leading architecture: The integrated management and control system is based on the cloud-native and micro-service architecture, which greatly improves the management capability, increasing the number of managed equivalent NEs from 30,000 to more than 300,000.
—Closed-loop O&M: Through the closed-loop operation of three engines, it offers full life cycle of intent creation, perception, and assurance.
—Various scenarios: It supports various network scenarios, including basic network deployment, multi-service provisioning and key network O&M services (e.g. key service assurance, network optimization).
—Smart applications: It achieves real-time perception of network and service based on the advanced data collection technology, network/service/resource analysis, detection and prediction using AI and big data, and assurance of network and service quality as well as intents through network and service optimization, protection, and restoration.
—Open interfaces: Open interfaces enable it to collaborate with other systems to meet user requirements more flexibly.
Typical Application Scenarios
Intent-Based Service Provisioning
The traditional service provisioning requires users to enter the function window of the network management and control system and accomplish complex service parameter configurations. It has three major problems: dependant on manual configuration, resulting in heavy workload and long service provisioning time; high requirements for skills, increasing the chances of errors and lowering the solution success rates; and point-by-point configurations, leading to large manpower investment and high O&M costs.
It can be seen that the intent-based service provisioning offers clear benefits in four major areas:
—Easy configuration and automatic service provisioning greatly shorten service provisioning time and improve the efficiency by 80%.
—Automatic verification reduces the error rate, lowers the requirements for personnel and improves the success rate of service provisioning.
—End-to-end service provisioning reduces manpower investment and O&M costs.
—Service configuration is visually represented, improving the user experience.
Intent Management
The system can effectively manage the intents after intent-based services are successfully provisioned. All intents are managed in a unified way, with their names, types, and status clearly shown in a list. To view the details, users just need to click the selected intent. To modify or delete an intent, users can click the corresponding action button, and then click modify to go to a page for adding, deleting, or modifying devices, ports, and bandwidth information contained in an intent.
Through centralized intent management, users can operate and maintain the full lifecycle of an intent.
At present, ZENIC ONE has been put into commercial use by many domestic and overseas operators including China Mobile, China Unicom, China Telecom, A1 Belarus and Telefonica Columbia, and has won extensive recognition. It will play a greater role in facilitating 5G network development and accelerating network autonomy.