Unified Data Plane: A Cornerstone of AI+ Core Network
By introducing AI capabilities, the AI+ core network enables operators to transform from traditional traffic-centric operation to a differentiated, experience-centric model, while supporting the development of a more efficient and secure 5G/5G-A network. Unlike traditional 5G core network, it must support large AI model training, analysis, and inference, which require massive amounts of data—hundreds of times more than before. These data are scattered and isolated, covering user-level information (subscriptions, mobility tracks, service experience histories), network-level O&M information (NE topologies, performance statistics, alarms, and logs), and wireless-side data (cell loads and resources). Efficiently collecting, processing, storing, and managing these data silos has become a key challenge. This article introduces the unified data plane as a solution to this challenge.
The unified data plane refers to the construction of a network-intelligence integrated, massive, multimodal data storage and management system in the AI+ core network. It provides unified services for data collection, preprocessing, storage, and analysis, as well as training, inference, management, and data security for AI large models, facilitating the sharing of both data and models. Evolving from the integration of the unified data repository (UDR)/unstructured data storage function (UDSF) in 5GC and the analytics data repository function (ADRF) from the intelligent network storage system, it offers a new solution for data processing in the AI+ core network.
Unified Data Plane Architecture
The unified data plane architecture consists of six layers: data collection, data processing, data storage layer, data analysis, data management, and data bus (see Fig. 1).
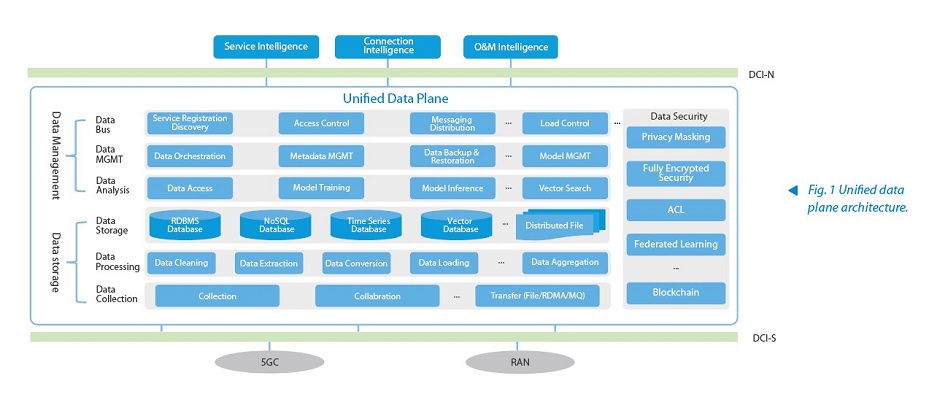
- Data collection layer: Collects data from 5GC, RAN, and other network entities in real time or periodically via the data collaboration interface-southbound (DCI-S), covering user-level, network-level, and cell-level data.
- Data processing layer: Performs data cleaning, aggregation, conversion and normalization to improve data quality and usability, supporting subsequent data analysis, AI training, and inference.
- Data storage layer: Stores preprocessed data in a large-capacity, scalable, and reliable multimodal storage system that supports efficient and highly concurrent access to differentiated data.
- Data analysis layer: Provides data training, inference, retrieval, and analytical functions, serving as a core component of the unified data plane. It uses the stored data to train AI models, for example, training an LSTM time-series prediction model using user mobility, NE load, and cell load data. The layer handles inference requests, applies the trained AI model for real-time inference, and predicts user behavior characteristics. It also supports vector search based on semantic similarity.
- Data management layer: Handles data orchestration, metadata management, data backup and recovery, and model management. It orchestrates data access procedures according to requests, establishes indexes, optimizes query parameters, performs regular backups to ensure data recoverability, and manages AI model updating, loading, and distribution.
- Data bus layer: Provides northbound data access and model invocation capabilities based on the DCI-northbound (DCI-N) interface for data-plane service registration and discovery. It also supports data and model access control and system load balancing and shunting management to ensure that only authorized requesters can access controlled data, improving network operation efficiency.
Key Technologies of Unified Data Plane
The unified data plane provides full-lifecycle management services for collecting, preprocessing, storing, analyzing, and opening massive data, as well as data security and compliance governance capabilities. The key enabling technologies include multimodal database engine technology, distributed computing and storage technology, and security and privacy protection technology.
- Multimodal database engine technology
The data stored and managed on the data plane varies in scale, read/write frequency, access performance, and persistence. Diverse database engines and file storage methods need to be adopted for multimodal storage. These include real-time transactional database engines such as RDBMS and NoSQL database engines; real-time analytical database engines such as time-series/columnar database engines; vector database engines; and distributed file or object storage—all aimed at maximizing both storage performance and capacity.
- Distributed computing and storage technology
The AI+ core network imposes high requirements on the data plane’s capacity, concurrent performance, and response latency, necessitating the use of distributed data storage and computing technologies. Distributed data storage technologies include distributed file storage and object storage systems such as HDFS, MinIO, and Ceph; distributed NoSQL databases and time-series databases such as MongoDB, Redis Cluster, Clickhouse; and ZTE’s cloud unified data repository (CUDR). Distributed data computing technologies include distributed computing frameworks like MapReduce and Apache Spark, along with distributed message-queuing and stream-processing platforms such as Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ, and FLink.
- Security and privacy protection technology
To ensure data security and prevent leakage, it is necessary to encrypt, store, and mask sensitive data; support access control lists (ACLs) to prevent unauthorized data access and model invocation; and support both vertical and horizontal federated learning. In addition, distributed trusted security management technologies, such as blockchain, should be gradually introduced to improve the security of data and models.
The unified data plane enhances the efficiency and reliability of data collection, management, and storage, while providing abundant data to improve AI model accuracy and generalization capabilities. At the same time, effective security and privacy protection measures are essential. As 5G/5G-A and AI evolve, the unified data plane must also advance to meet the growing demands of network intelligence. With ongoing innovation, the unified data plane will provide strong support for the AI+ core network.