With continuous development and wide applications of new-generation information technologies, digitization, networkization and intelligentization have become important directions of economic and social transformation and upgrade. The development and application of artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, cloud computing, and the Internet of things (IoT) all depend on data. Thus data has become a production factor and the basis of digital economy. Data in the digital era can be compared to petroleum in the industrial era. However, unlike petroleum, data is intangible and infinite, and there is a huge amount of data being generated every minute. How to make good use of data to create value has become the key to success in the era of digital economy.
Data driving development does not mean that data can be automatically turn into productivity. The value of data cannot be achieved without the corresponding data infrastructure, including facilities involved in data collection, transmission, storage, and computing. New infrastructure, such as new networks, facilities, platforms, and terminals, needs to be built. Neuron systems for data collection need to be built based on the ubiquitous deployment of smart terminals. High-efficiency data transmission networks need to be built based on the full coverage of new 5G networks. Data computing capabilities need to be improved based on computing facilities such as Internet data centers and high-performance computing (HPC) centers. Intelligent data analysis centers need to be built based on the development and application of AI platforms, industrial Internet platforms and IoT platforms.
Looking at the nature of data driving, a data center carries the computing power and transforms data into intelligence, while a network is the key infrastructure that transmits the computing power to users and transforms data into value.
Data-Centric Network: Architecture and Vision
The overall architecture of the new data-centric network is shown in Fig. 1.
Horizontally, the data-centric network architecture complies with the end-to-end empowerment principle of service-based networks. That is, the end-to-end Internet protocol-based architecture is maintained, and the services are mainly processed on the two ends. While improving core capabilities (such as deterministic transmission, native security, and computing power scheduling), the network opens these capabilities in a hierarchical manner with different granularities for the service layer to use.
Vertically, the architecture adopts the thin-waist model supported by the intelligent control plane. That is, the "thin-waist architecture" of the Internet protocol stack is retained. The IP layer is kept stable enough to extend new functions with the existing IP fields. Network function extension (mainly for the operator's data network) is performed on the centralized control plane with effective use of new IT technologies such as AI and big data.
For deterministic and secure transmission of computing power, a data-centric network needs to have three key features: large-scale determinacy, ubiquitous service, and zero-trust native security (Fig. 2).
Large-scale determinacy means that the IP network with a large number of devices can support up to millions of data streams (such as massive industrial-level control and sensors) and provide deterministic service guarantee, with the latency and jitter strictly meeting service requirements. The industrial Internet also needs cross-WAN end-to-end determinacy. Based on native IP, the large-scale deterministic IP network proposed by ZTE implements periodical forwarding and accurate scheduling on the new-generation 5-nm chips. End-to-end jitter can be guaranteed no matter how large the networks are.
Native Security
To meet the security requirements of future networks, ZTE is committed to building native security and reliability mechanisms. Using blockchain and cryptography, it redesigns the future network architecture, provides end-to-end services from infrastructure to application layer, and builds a complete set of secure and reliable network architecture from bottom up. In this way, using zero-trust security mechanism ZTE endows the network with secure and credible attributes and capabilities in the "gene" of the network to provide a more solid security foundation for future network protocol systems and network services. This fundamentally solves the security problems that today networks face and evolves the security system from superposition security to zero-trust native security (Fig. 3).
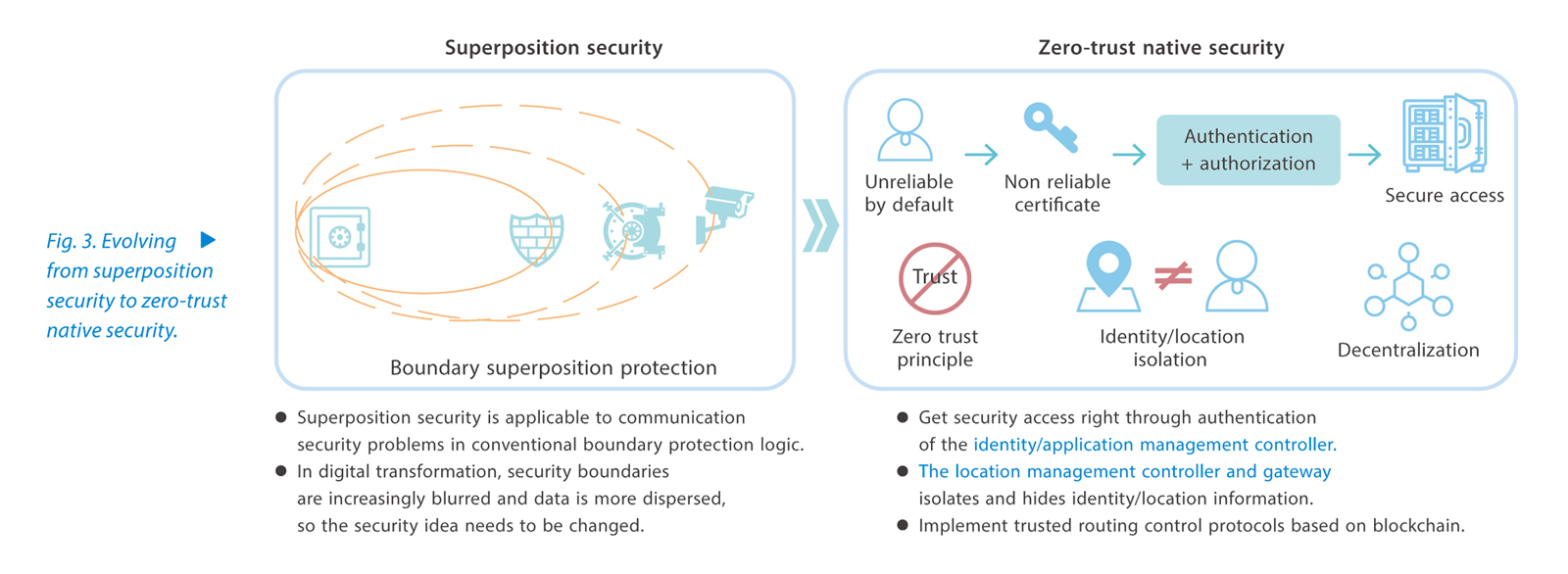
The idea of ZTE native security is as follows: horizontally, the security of the communication source end and destination end is handled. The intelligent plug-ins residing on the ends (including terminals or edge nodes) complete the initiation and termination of network trusted communication, and the remaining intermediate nodes perform transparent forwarding. Vertically, the intelligent control plane based on big data and AI provides real-time threat detection and intelligent determination as well as large-scale network security indicator evaluation and prediction to monitor network behaviors and prevent risks. The data plane integrates trusted network communication into the unified network layer protocol.
Ubiquitous Service
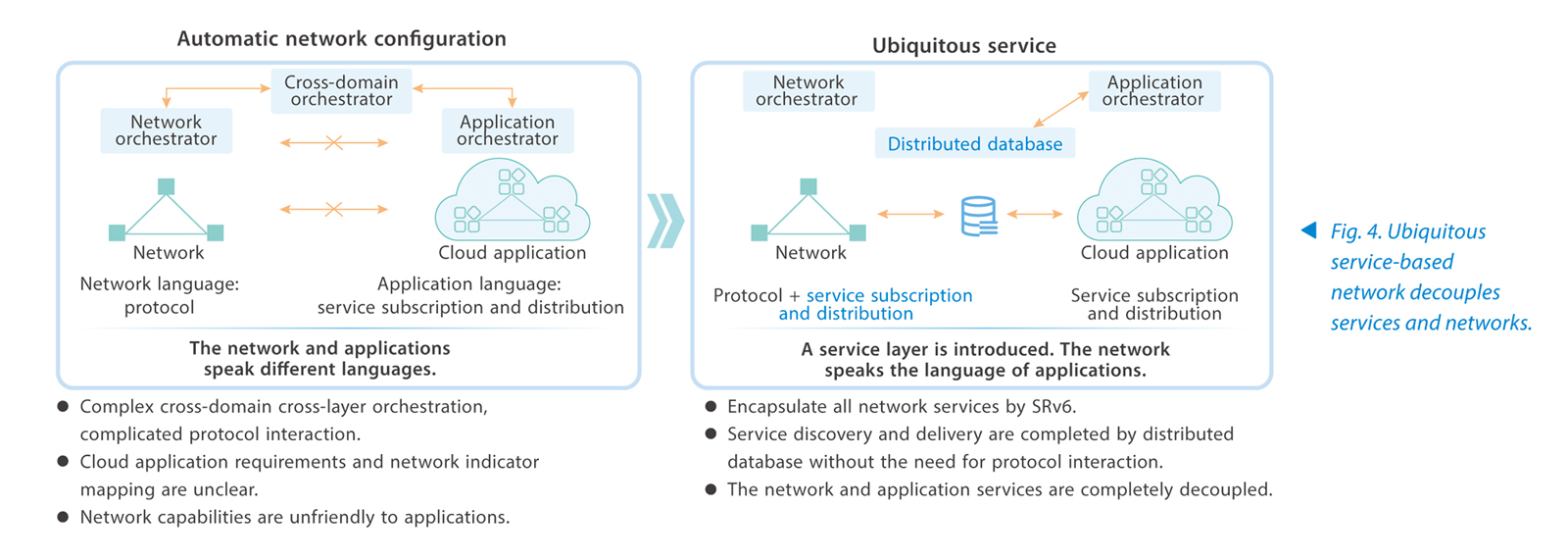
In the future, cloud-network convergence is an inevitable trend, and dynamic network adjustment with the cloud is an inevitable requirement. Although automatic configuration has been implemented on the network side, which simplifies network operation and maintenance, the fundamental problem has not been solved. In the traditional network and application peer-to-peer model, the network and applications speak their own languages. The network and applications need to intact with each other through complex protocols and cross-domain cross-layer orchestration. As a result, the network is not agile enough to meet the requirements of substantial industry applications.
ZTE proposes a service-based network model, which adds a service layer between the basic network and applications to build a ubiquitous service-base network that is loosely coupled, highly scalable and easy to maintain. The ubiquitous service-based network encapsulates network capabilities such as VPN, TE, service chain and security into services, and pushes them to the applications through distributed databases. Lightweight network services directly communicate with the applications. The applications only need to focus on their own requirements without caring about specific implementation or supporting complex protocols and network interaction. The ubiquitous service-based network removes complex protocol interaction and cross-domain cross-layer orchestration between the network and applications, and encapsulates all network services through SRv6. The discovery, delivery and update of network services are completed by the distributed databases. This completely decouples the network from applications, providing the most open cloud-network convergence capability and the most extensive access capability (Fig. 4).
Summary The data-centric network model can deeply reveal the essential role of the network and its value in the digital economy era. The network is responsible for secure and deterministic transmission of data, and provides service-based lightweight interaction, thus greatly improving the cloud-network convergence capability.