As 5G services develop rapidly, operators pay more attention to deep indoor coverage deployment. On the one hand, 5G indoor data services account for 90% of total data services, which raises higher capacity requirements for indoor networks. On the other hand, the network analysis of some tier one cities in China shows that insufficient indoor coverage is the main factor for high backflow ratio of 5G traffic, and more than 85% of complaints about poor 5G signals or slow 5G speeds occur in indoor scenarios. It is therefore important to extend indoor 5G coverage.
The traditional passive distributed antenna system (DAS) has low capacity when directly upgrading to 5G, while the high-performance digital active DAS represented by QCell is expensive. Balancing cost and performance in a variety of indoor scenarios is a major issue to be addressed. ZTE has proposed its hierarchical DAS collaboration solution that can achieve the best balance between cost and performance through the collaboration within the same DAS and between different DASs, giving operators the flexibility of deploying their 5G indoor coverage.
eDAS Reuses Existing DAS and Improves Performance to Meet Low-Cost Needs in Low-Value Scenarios
Passive DAS has a huge established market with mature technologies and low costs, and is easily shared by multiple operators with multiple frequencies and modes. However, it has the disadvantages of low capacity, poor user experience, and difficulty of offering higher-order MIMO by adding more feeder channels to existing DAS. In the 5G era, how to reuse the existing DAS system to achieve faster and more cost-effective indoor 5G coverage is still a major concern of operators.
ZTE's eDAS uses the following key technologies to make up for the disadvantages of passive DAS:
—For a typical 2T2R DAS system, two 2T2R RRUs with antennas and feeder channels for two adjacent cells can be collaborated to achieve a virtual 4T4R network in overlapping areas without the need to deploy any new antennas and feeder channels, thus reducing interference between cells and enhancing network performance.
—The innovative 5G algorithm is used to reduce the negative impact on MIMO performance caused by unbalanced signal transmit power between different DAS channels.
eDAS can reuse the traditional DAS system architecture, which greatly saves costs and avoids the often painful site location acquisition. Only by deploying the software version, single-channel DAS dual-stream and dual-channel DAS four-stream can be easily achieved, which considerably improves the performance of traditional DAS network. eDAS is also compatible with 5G terminals and has no restrictions on the terminals.
Collaboration of Passive DAS and QCell Achieves Smooth Capacity Expansion and Quality User Experience in Middle-Value Scenarios
The existing passive DAS can be upgraded to support 5G, but it still faces the capacity challenge brought by rapid growth of 5G services. 90% of existing DASs only support 1T1R with a single feeder channel, and even if they are upgraded to 2T2R, the capacity increase is still limited. The distribution of indoor traffic is unbalanced. 80% of the traffic occurs in 20% of the indoor areas, and the traffic will increase with the growth of customer services. However, capacity expansion for passive DAS is difficult because it has to replan, combine more additional RRUs and re-adjust feeder connection, resulting in higher costs and longer cycles.
To solve the challenge of passive DAS expansion, ZTE has proposed the collaboration solution that leverages the coverage advantage of passive DAS and the capacity advantage of QCell. For example, in a shopping mall or office building where passive DAS systems have been deployed, QCell can be deployed directly in areas where capacity enhancement is needed such as shops or VIP conference rooms. To ensure that QCell works normally and is not interfered by co-channel DAS signals, it is usually necessary to adjust the DAS system in the corresponding area and disable DAS signals in this area, which brings not only difficulties in engineering and network optimization but also poor experience to users. ZTE's collaboration solution solves the problem of different signal transmit power and transmission channels between different DAS systems, turns interference into gain, simplifies the overlay deployment of QCell, and effectively improves the capacity and user experience in hot spot areas. In addition, it can reduce handover and interference to improve user experience at the junction of passive DAS and QCell, such as the areas between elevators and halls or between subway tunnels and platforms.
SuperMIMO Boosts Capacity in High-Value Hot Scenarios
Digital active DAS such as QCell has the advantages of simple deployment, scalability and manageability, and can better meet the needs of future service development, so it has become a preferred choice for high-value scenarios. With the growth of 5G services in high-value scenarios, QCell can split few cells to meet the capacity requirement. However, as the number of split cells increases, inter-cell co-channel interference increases dramatically. When the interference reaches the threshold, system capacity is saturated, cell splitting cannot improve capacity, and user experience becomes worse. ZTE has developed the SuperMIMO solution for Qcell, which collaborates multiple distributed antennas of QCell as one massive MIMO antenna to serve a single UE or multiple UEs in a cell. In this way, user signals are enhanced while solving the problem of co-channel interference. This improves user experience and cell capacity, and addresses the contradiction between interference and capacity.
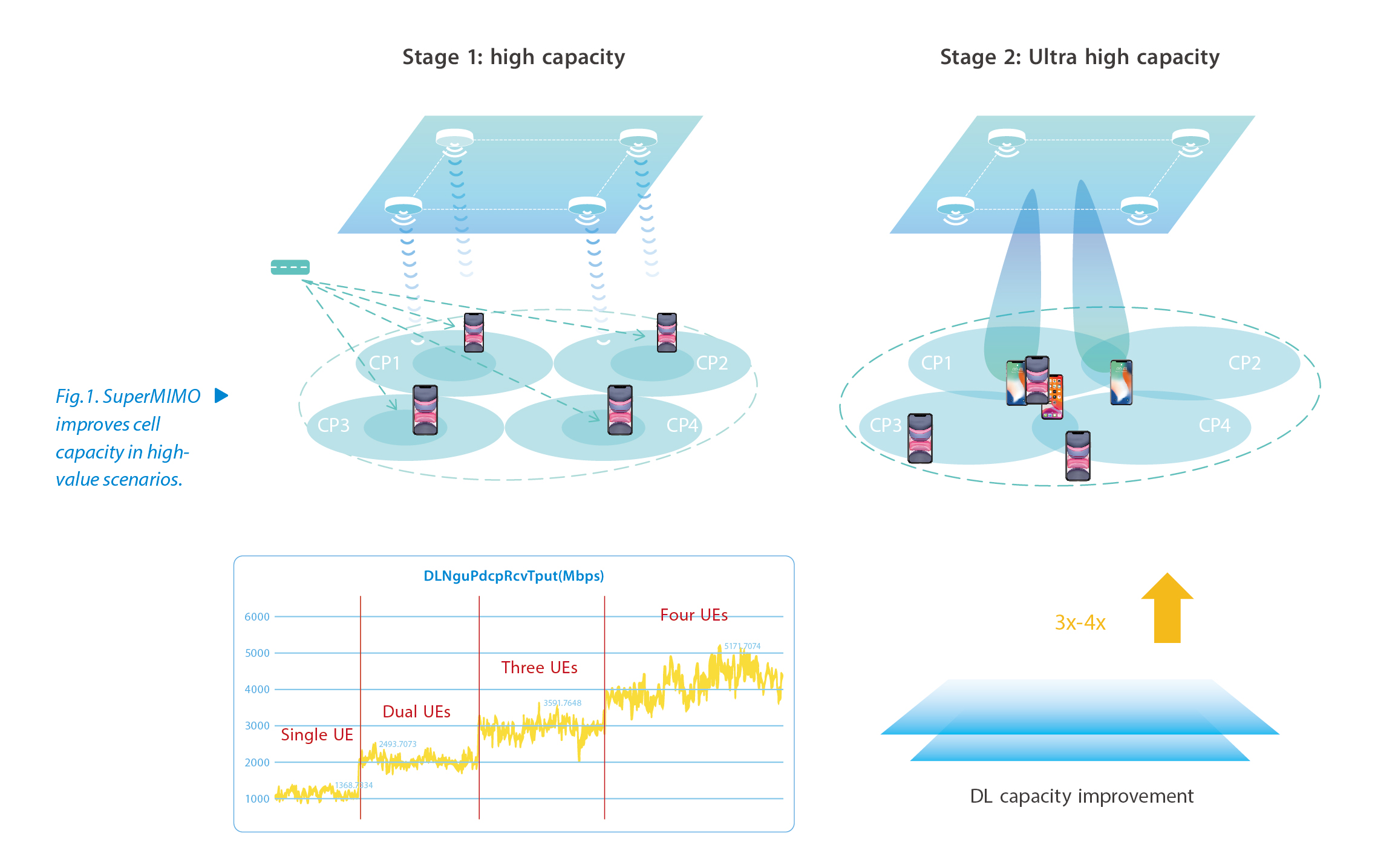
To accurately match the high capacity and ultra-dense capacity requirements in network development, SuperMIMO is planned into two technical stages (Fig. 1). For high indoor traffic scenarios, the super cell technology is used to reduce multi-cell interference and handover, and the system automatically performs space division pairing for multiple UEs to enhance cell capacity. For the UEs in the overlapping area of edge signals, the number of MIMO layers can be increased by collaboration of adjacent multi-antenna transceiver solution. For the scenarios with extremely high traffic, ultra-dense user distribution and poor spatial isolation, it is necessary to achieve accurate beamforming gain and MU pairing to improve cell capacity through the collaboration of QCell's distributed massive antennas.
Currently, eDAS has been commercialized on a large scale in more than 10 provinces in China such as Guangdong, Beijing and Shandong. It makes full use of the existing DAS, improves performance by 35% in the downlink and 25% in the uplink, and reduces the cost by 80% compared with the newly built DAS. SuperMIMO has also been widely used in metro, airport, hospital and shopping mall in more than 10 cities in China such as Guangzhou and Shenzhen, and has increased cell capacity by three to four times. With efficient collaboration and flexible deployment, the hierarchical DAS collaboration solution can help operators significantly improve indoor network performance, reduce network construction costs and build quality 5G indoor coverage networks.