Simplified 5GC Solution Speeds up 5G Development
Network Innovations Call for a New Core
5G will enable a diverse array of services and meet varying connectivity need. The three major application scenarios defined by ITU for 5G include eMBB, uRLLC and mMTC. To meet the needs of these scenarios, 3GPP has defined a new 5G core network (5GC), featuring service-based architecture, network slicing, CUPS and stateless function, as well as two architectural options (5GC and EPC) to adapt to different wireless deployment scenarios.
●5GC: Depending on wireless deployment mode, a 5G new radio (NR) base station and a 4G eNodeB are independent from each other or mutually dependent. The 5G NR directly connects to the 5GC or serves as a secondary RAT to access the 4G eNodeB; the UE is in single connection or dual connections with the 5G or 4G RAN.
●EPC: This is a non-standalone deployment based on the existing 4G core. The 4G eNodeB serves as the anchor RAT and the 5G NR as the secondary RAT; the UE simultaneously connects to the 5G NR and 4G eNodeB; and the 4G/5G interoperability is achieved through RAN.
Operators can select different core network architectures according to their commercial 5G deployment plans, available spectrum resources, the maturity of terminals and industry chains, and TCO.
5G is targeted at coping with the OTT challenge, exploiting the vertical industry, and increasing revenue streams for operators. It should be capable of rapid customization, slice-based network operation, and highly-automated, intelligent O&M. The 4G EPC based on the traditional architecture cannot meet those requirements. The cloud- and SBA-based 5GC is the target 5G network architecture. Its advanced network architecture can help operators avoid overlapping investments, frequent network transformations and achieve a leading market position. The 5GC with SBA is a one-step-to-reach approach to architecture, and makes centralized construction and intensive O&M easy. With the support for FMC, it also facilitates the introduction of big data and AI to improve the level of network intelligence. By leveraging the 5GC, operators will be able to expand cooperation with industry verticals and quickly roll out new services. Therefore, adopting a 5GC architecture is aligned with world-leading operators’ goal for strategic innovations and the needs of 5G commercialization.
Challenges on the Way to Innovation
As a brand-new core network, 5GC adopts new technologies and is naturally accompanied by various challenges and speculations. Only by facing challenges and finding solutions can an operator stand out from the market competition. Considering the needs of commercial 5G deployments, building a new 5GC has three major challenges: network deployment, network function, and new service development.
Network Deployment
Virtualization is central to 5G. All the new 5GC-enabling technologies are based on virtualization. The virtualized 5GC built around the COTS severs maximizes resource sharing, and operators can enjoy the benefits of Moore’s Law (i.e. performance improved by 30% at least every 18 months). 5GC is based on the VM or container technology, and the brand-new SBA and interfaces. It uses a lot of horizontal and vertical interfaces. When operators test new network functions, they have to complete the interoperability tests between horizontal and vertical interfaces. Therefore, how to fast deploy a commercial 5GC based on virtualization and SBA is a big challenge.
Network Function
A 5G network provides many service functions, mostly related to key functions such as user data and billing. For user data, full convergence is the goal of network construction. Operators have to consider how to implement the network migration from 4G to 5G so that users don’t have to change their SIM cards or phone numbers. With respect to billing, there is a big difference between the target converged online/offline charging system based on the SBA and the existing architecture with online/offline separation based on traditional equipment. The challenge is to how to rapidly put the convergent billing system into commercial use while achieving compatibility with the existing billing system.
New Service Deployment
Network slicing is a critical service for 5G. It is a key technology for operators to adapt to different service needs and scenarios and build new profit models. For the differentiated requirements from vertical industries, government and enterprise customers, and low-latency ISPs, how to flexibly divide a network into slices is the key challenge for network slicing deployment. Voice and SMS services will continue to be essential in the 5G network, for which, several solutions have been defined by 3GPP. It is important to find out which solution allows speedy deployment of 5G voice and SMS services while having the least impact on the existing network, and how to ensure service continuity and quality.
Simplified 5GC Solution
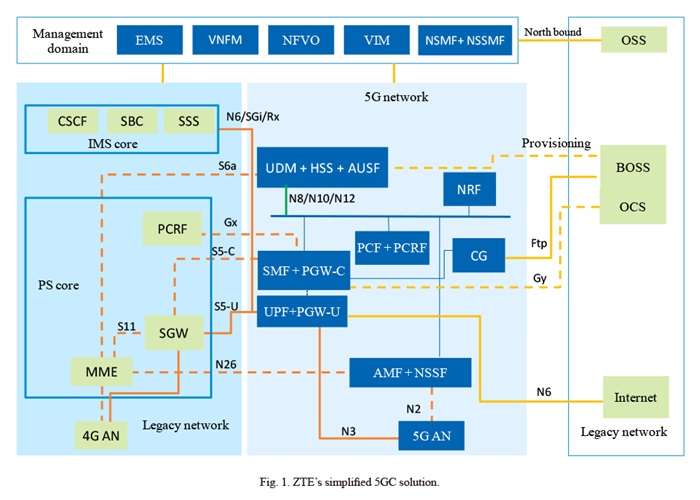
ZTE proposes a simplified 5GC solution (Fig. 1) to help operators gain a lead in 5G network construction and benefit from 5GC’s new technologies.
Streamlined Deployment
At present, traditional networks are due for an upgrade and are no longer suitable for large-scale investments. Industry-leading operators are actively promoting the commercialization of virtualization. The deployment of 5GC can speed up virtualization, and it often uses the following concepts :
●Centralized deployment of control plane: Centralized deployment of 5GC control plane helps unify services across the whole network, develop slice-based services, and achieve centralized and intelligent O&M to reduce Opex.
●Layered and phased deployment of user plane: The user plane can be deployed in centralized mode for early-stage 5G deployments. A layered approach will be adopted at the middle and later stages with the user-plane functions deployed close to the access network as needed to reduce latency and improve customer experience. User plane virtualization allows resources to be shared across layers, solving the holiday tidal effect.
●Phased construction of 5GC NF: At the early stage of 5G, basic NFs can be deployed, and optional and unimportant NFs deployed later as needed. At the early stage, 3GPP-compliant 4G/5G convergent NFs can be deployed for interoperability, and more NFs deployed later to achieve full convergence of 4G/5G NFs.
●Phased opening of interoperability interfaces: At its early stage, the 5GC needs to open interfaces for subscription, RAN, UE, 4G/5G interoperation, network management and billing to reduce testing and deployment time. More interfaces should be gradually opened to achieve features like international roaming.
Simplified NF
To build a 5GC, it is necessary to deploy convergent UDM+HSS for unified, centralized management of 2G/3G/4G/5G user subscription data. At the early stage, data migration can be carried out for users who have upgraded from 4G to 5G. At the middle and later stages, the existing 4G users will be gradually migrated to the new convergent UDM+HSS, depending on the aging degree of legacy HLR/HSS. The flexible number routing (FNR) scheme is used to solve the call routing problem of users with discrete number sections at the initial stage.
To support 4G/5G interoperability, the 5G SMF and 4G PGW-C will be converged. At the early stage of 5G, 4G billing interfaces, which are supported by the convergent SMF+PGW-C, can still be used. This avoids large transformation work and delay of commercial 5GC use that might be caused by the introduction of 5G billing system.
Simplified Service Deployment
At the early stage of 5G with limited industrial applications, it is preferred to perform sub-slice management first in the core network, and then gradually carry out slice trials and verifications based on the 5GC. The initial focus is on eMBB slice services such as HD video, AR/VR and HD game, and with the 5GC user plane moved to the edge, the demands of some ultra-low latency services will be met. At this stage, the ability of slices to fulfill the differentiated SLAs can be verified, so as to set up exemplary industrial applications. With the maturity of 5G slice standard, transmission/wireless sub-slices will be gradually introduced. Based on the orchestration and management system constructed in the previous stage, the 5GC will add the functions of slice design, assurance analysis, and policy management, and provide the life-cycle management of E2E slices. It is necessary to consider network slice operation, including slice delivery, pricing, billing, and opening of capabilities, accumulating operational experience and related technologies for slicing commercialization.
The 5G voice standard defined by 3GPP R15 has been mature, and commercial 5G terminals will reach the market in 2019. Mainstream operators have deployed IMS networks to support VoLTE. At the early stage of 5G with only hotspot coverage, to reduce the voice handover between 5G and 4G, it is preferred to upgrade the software for IMS and perform 5GC EPS fallback for VoLTE. Along with the expansion of 5G coverage, VoNR can be used to provide 5G voice services.
E2E 5GC Products
5GC is the key technology for 5G network construction and service bearing. ZTE’s core network products address the urgent needs of the world’s leading operators to construct a 5GC with advanced architecture and innovative technologies. Based on previous simplified solutions, ZTE provides the following products to meet different deployment demands.
CloudStudio (O&M system): It is the ZTE 5G oriented O&M system that will continuously optimize user experience and networks with its self-evolution capabilities (design – deployment – operation – analysis – redesign). In the future, it will introduce AI and machine learning to achieve intelligent policy prediction, a more intelligent system, and zero-touch operations.
Common Core (5G convergent core network): It is the ZTE fully convergent 5GC product, which is based on SBA and supports mobile access (2G/3G/4G/5G) and fixed access (trusted and un-trusted non-3GPP access).
Tulip Elastic Cloud System (TECS): It is the ZTE cloud platform product that provides 5G-ready VIM and NFVI functionalities and creates a robust and reliable infrastructure for operators.
Considered the brain of 5G network, 5GC directly impacts the realization of operators’ network innovation strategy. ZTE’s simplified 5GC solutions and products speed the way to 5G deployment and help operators step into the 5G/IoE era.