Magic Quadrant for Small Cell Equipment
The macrocellular networks that communications service providers (CSP) deploy often fail to meet the needs of users, mobile operators and location owners. We assess 16 vendors of femtocell, picocell and carrier Wi-Fi equipment that can remedy this shortcoming and give guidance to network planners.
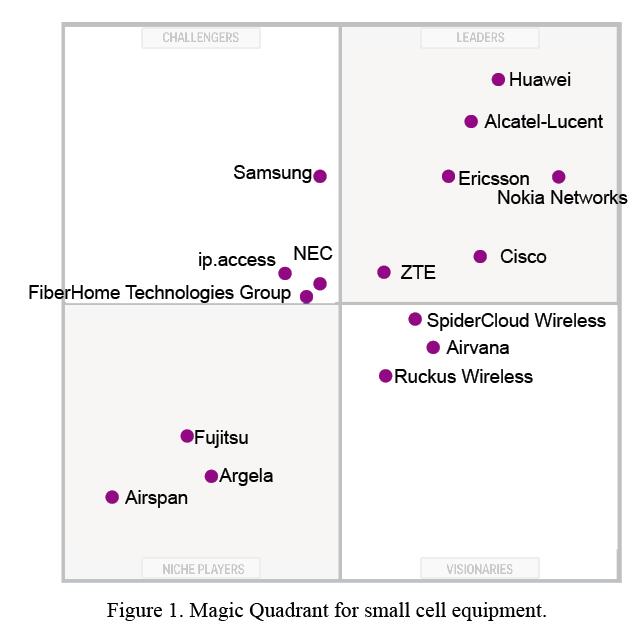
Market Description
The small cell market, including carrier Wi-Fi equipment, is growing in terms of interest, numbers of connected users and product revenue (up 44% year over year).
Increasing numbers of smartphones, tablets and similar devices, together with the proliferation of video consumption and the transition from 3G to LTE networks and services, are contributing to high growth in data traffic. A common short-term approach to coping with this growth has been to offload this traffic onto unmanaged Wi-Fi networks. However, CSPs should look to improve customer experience by keeping subscribers on their cellular networks, an aim they could achieve using a combination of picocells, femtocells and carrier-class Wi-Fi equipment.
Usage of small cells is driven by changing patterns of user traffic. The vast majority (70% to 90%, depending on the geography) of subscribers' data traffic arises when they are indoors, but many LTE and 3G frequencies are poor at macrocellular indoor coverage, which means subscribers receive a "cell edge" experience that reduces effective cell capacity and bandwidth and also significantly shortens device battery life. In most cases, increasing the density of macrocells is not a cost-effective solution, and traditional distributed antenna systems are cost-effective for only the largest venues and solve the coverage issue rather than the capacity issue. Hence, CSPs are increasingly interested in small cells.
The small cell market comprises outdoor picocells, indoor picocells, residential femtocells, enterprise small cell solutions and carrier Wi-Fi equipment, about which the following points may be made:
● CSPs will use outdoor picocells to augment macrocellular networks in city centers and other points of network congestion. Outdoor picocells can also improve cellular coverage in rural areas much more cost-effectively than macrocells.
● Public Wi-Fi access has become more popular in locations such as shopping malls, transportation hubs and hospitality centers, and CSPs are starting to complement this with indoor picocells.
● CSPs continue to deploy residential femtocells in areas of poor coverage.
● Deployments of enterprise picocells and femtocells have started to grow in 2015 as bring your own device (BYOD) schemes and secure cloud services fuel demand for improved cellular services in office environments. Gartner's research shows that 30% of calls made by enterprise employees at their desks are on mobile phones, but many LTE and 3G frequencies are poor at macrocellular indoor coverage, with the result of patchy coverage and shortened device battery life.
CSPs are starting to see opportunities in value-added services delivered over small cell infrastructure, such as managed unified communications (UC), IP PBXs, presence sensing, real-time analytics and caching. Most CSPs now require integrated Wi-Fi in their femtocell and picocell deployments.
Many CSPs agree that there is no single technical solution for all requirements, so most plan to take a multivendor approach. However, other CSPs are concerned about integrating a third party's network equipment into their existing macrocell and core network, so they tend to take a single-vendor approach, which, in turn, can limit their small cell designs. The vendors in this Magic Quadrant offer a range of features. Some focus on one or two market areas, while others try to cover all options. Some provide a suite of professional services, ranging from optimizing cell locations, network planning and installation through to neutral hosting, while others focus on equipment sales.
Different types of equipment have different features, options and requirements with regard to networks and integration; however, power consumption, size, ease of installation, integration into the macrocell network, user capacity and frequency bands of operation are common considerations:
● Femtocells used by CSPs for residential and small or midsize business (SMB) settings are often self-organizing networks and "plug and play", and have highly scalable femtocell gateways. Competitively priced and reliable products are key. CSPs should also consider whether they need features such as presence sensing and processing capability to support additional services.
● Enterprise small cells can be single cells or multiple distributed cells. They can be stand-alone and self-organizing or synchronized with a macrocellular network. They may also be able to operate on existing LAN infrastructure, or they may require specific cabling, such as CPRI fiber connections. Features such as multiple frequency band support, multioperator support, and support for applications such as presence sensing and local analytical processing are among the available options.
● Outdoor picocells can be either parts of a heterogeneous network or stand-alone products.
● Wi-Fi equipment can be stand-alone, or can be integrated into femtocell and picocell equipment. Carrier-class features include cloud controllability, dual-band operation and support for Hotspot 2.0. CSPs should choose highly scalable gateway controllers to integrate Wi-Fi traffic into their core networks.
Please note that vendors disclose the number of customer engagements in different ways, and the numbers given in some of the vendor profiles within this report should not be directly compared. Numbers are as of September 2015 but can be expressed as either number of CSP customers or number of small cell projects within CSP customers. Numbers may include regional projects and may or may not include carrier Wi-Fi deployments.
Vendor Strengths
ZTE
ZTE has made significant advances in its small cell products and strategy since last year's Magic Quadrant, and as a result, it has accelerated its product shipments. China, its home market, is a strong source of sales, but the company also has had success in Europe, Japan and Malaysia. ZTE has a product range that includes home and SMB femtocells, indoor and outdoor picocells, and its Qcell distributed radio solution for large enterprises and venues. ZTE's products support 3G and LTE, FDD and TDD, Wi-Fi and LTE-A carrier aggregation, and up to 256 QAM. ZTE supports HetNets and plug-and-play installation for its indoor products. The company now understands the need for new business models for the indoor small cell market, and it is building industry partnerships to help facilitate growth in installations. ZTE's services can provide an end-to-end small cell solution.
ZTE has a wide range of small cell solutions, and its Qcell has been well-received and is deployed in shopping malls and universities. The product can support four frequency bands and up to two CSP networks per CPRI cable.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
To qualify for this Magic Quadrant, a technology provider must satisfy one of the following two criteria:
● The technology provider must have shipped small cell products to CSPs during the 2014 to 2015 period.
● The technology provider must have achieved significant mind share in the small cell market segment, either through its visibility in terms of publicly announced small cell contracts or through its new innovative small cell products.
Evaluation Criteria
Ability to Execute
In this Magic Quadrant, we assess vendors' products and professional services, and their ability to meet the needs of today's market. We rate the overall viability of a vendor's small cell business unit and the company as a whole, to provide an opinion on the relative merits of the vendor as a supplier. We gauge how successful the vendors' product sales have been, as well as the merits of their sales structure. We also consider vendors' responsiveness to customer requirements, together with feedback from reference customers.
Completeness of Vision
We evaluate the vendors' understanding of the market's dynamics and the changing needs of service providers, partners, channels to market, subscribers, enterprises, property owners and other parties that are becoming part of the small cell ecosystem. We also assess how well vendors' marketing strategies align with their core strengths. The vendors' approach to product and service development is an important consideration, together with the features they plan for next-generation solutions. Innovation is a key aspect on which we measure vendors, along with the solutions they propose to differentiate themselves in the market, and how they plan to overcome the obstacles and issues that hinder market development and customer satisfaction. Finally, we take into account vendors' geographical strategy and how they address a global market.