Mobile Networks in the Big-Data Era
Over the past few years, the telecom industry has undergone great changes and operators have had to adjust. The growth of mobile user base has slowed down. This has done little to boost operator revenue. Data services are growing at unprecedented rate, and the co-existence of 2G, 3G, and 4G networks has made network management much more difficult. People are also increasingly relying on mobile internet and are more sensitive to network QoS. Therefore, network QoS has become an important factor affecting an operator’s business growth.
Such changes pose great challenges to operators, who are pressed to offer faster, more flexible network management mechanisms, become more efficient, and meet fast-changing user needs with innovative ideas.
Network operation is now being viewed from multiple dimensions, not in the traditional way where market expansion was viewed separate from network O&M. Multidimensional network operation means that network, services, and user data correlated and analyzed holistically. O&M must guarantee network services but also guide market expansion and increase operational efficiency. Existing O&M systems do not satisfy user needs because they are designed to solve specific problems rather than analyze end-to-end user data and experience. Moreover, existing systems do not support centralized management and analysis of ultra-large networks. So using big-data technologies to integrate all network data resources for in-depth correlation analysis has become a crucial way for operators to meet market challenges.
ZTE's Big-Data Solution
Drawing on years of expertise in O&M, ZTE has developed a wireless big-data solution based on its Hadoop system (Fig. 1).
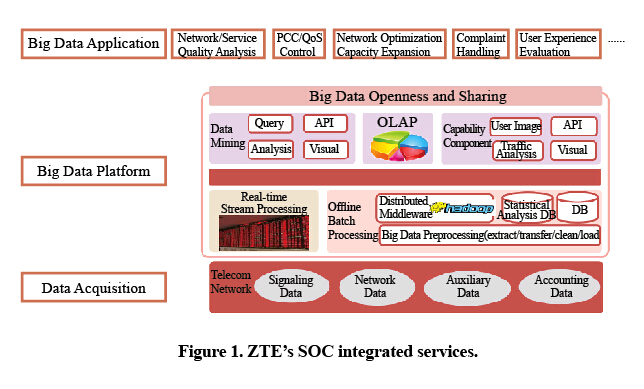
The wireless big-data solution consists of three layers:
1. data acquisition. Data is the foundation of ZTE’s wireless big-data solution. Data richness and integrity affects the result of upper-layer analysis. ZTE’s big-data solution supports interoperability of various systems in 2G, 3G and 4G networks and uses a probe to collect data from the control and media planes via Gn, IuPS, Gi, S1, and S10 interfaces.
2. big-data platform. A huge amount of network data is stored on this platform, which is the core of the solution. Using big-data technologies, the platform is capable of offline batch analysis and online real-time analysis of mass data. The platform also supports a variety of data analysis, mining, and visualization tools for upper-layer applications.
3. Big data application. In this layer, network quality, service quality, user experience, and network planning and optimization is visualized through user-centric data analysis and mining. This helps an operator handle customer complaints quickly and increase operational efficiency.
Big-Data Application Scenarios
ZTE’s wireless big-data solution guarantees:
● optimal resource allocation. During network deployment, operators need to make full use of existing data. Limited resources are allocated to the neediest areas to make resource utilization more efficient.
● network optimization. High-quality networks are essential for normal business operation. Various network data sources can be analyzed so that O&M personnel can find out the root cause and troubleshoot problems quickly.
● service quality. As networks evolve, services are becoming more complicated. Therefore, the focus of network O&M has shifted from overall network KPIs to the quality of specific service. Faulty services can be located through end-to-end service data analysis and according to specific service features. In this way, faulty services can be fixed and QoS can be improved for the user.
● good user experience. KPIs alone do not fully reflect user experience. QoE is more thoroughly determined by evaluating services end to end. In this way, services creating poor user experience can be fixed.
The solution also includes:
● network evaluation consulting. This helps an operator determine the network status and identify potential problems. It enables an operator to optimize existing networks and devise future development strategies.
● network development consulting. This helps an operator devise network development strategies while protecting their existing investment. This helps optimize overall ROI.
● service development consulting. Different services have different value to an operator. Service development consulting involves assessing the value of services according to current usage and offering suggestions on how to promote services and increase network value.
● Market strategy consulting. This involves evaluating user needs, resource use of various services, and their contribution to network in order to guide an operator to marketing success.
Customer Value
ZTE’s wireless big-data solution enables end-to-end data analysis. This helps an operator integrate the front-end market with the back-end network and makes operations more efficient.
Determining Network Status Clearly and Accurately
Traditional O&M systems often determine overall network status according to part of the network. Big-data applications, however, enable an operator to determine network operation, service operation, and user experience from a whole-network perspective. This helps an operator optimize network configuration and fully utilize network resources.
Utilizing Big-Data Resources and Mining New Value
In mobile networks, a large amount of data reflects not only network status but also user preferences and location. Analyzing and mining all this information helps an operator expand their business and marketing opportunities and provides other industries with necessary guidance. At present, this belongs to a new field in which industry is groping its way forward.
The value of big data to the telecom market has long been known. According to Sysbase, the telecom industry is the biggest beneficiary of big data. Operators derive value from data-mining and have experienced the greatest boost in sales from it (Fig. 2).
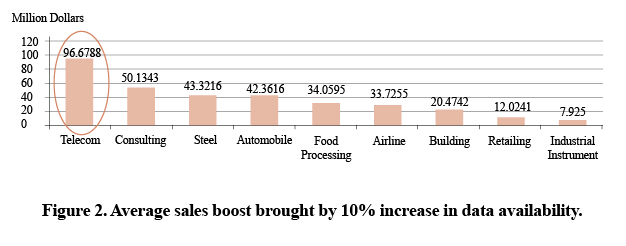
The value of data has been noticed in all fields, but the internet is ahead of the others in data-mining. Network operators also have abundant data resources and need to efficiently integrate decentralized data. Through multi-party cooperation and innovative service products and business models, operators will continue to use and extract value from big data.