M-ICT: Creating a New Era of Mobile Internet of Everything
The office mode has evolved from PC + internet to cloud + terminal. Interpersonal communication is also changing to communication between people and things, things and things. All these indicate the coming of a new era.
In this era, science and technology is becoming more people-oriented. In the beginning, technological innovations were large, expensive and very attractive. Along with the progress of science and technology, they are more invisible, tiny, and cheap. People are starting to pay more attention to meeting their needs with science and technology rather than “science and technology itself”. These characteristics have been well reflected from the development of CPUs and mobile communications: The processing capacity of a 4G base station is several orders of magnitude higher than that of the earliest base station, but the volume of the 4G base station is several orders of magnitude smaller than the earliest base station and is no longer attractive.
Features of the M-ICT Era
● Feature 1: Ubiquitous connection. By 2020, there will be more than 50 billion connections. The ubiquitous connection is formed by man-to-man, man-to-machine, man-to-information, man-to-service, and physical world to cyber world connections. Everything is connected, and everything is smart.
● Feature 2: Ubiquitous service; life and work with the same experience. The commonality of mobile smart terminals covering the consumer and business markets has gradually appeared. In both life and work, people want consistent service. With the rapid development of internet and cloud computing, cloud services are ubiquitous, and everything is reachable.
● Feature 3: Integrating the physical and cyber worlds. The cyber and physical worlds are combined technologically and economically. Consumers are eager to open the door of O2O business. The real economy lags behind the virtual economy in terms of innovation. By combining the real and virtual economies, the technological and market boundaries of the internet and ICT are greatly expanded into traditional industries, developing them in green, healthy, open and efficient directions.
● Feature 4: Attention is paid to security and privacy. Security and privacy have never received more attention than they have today. Whether national and governmental confidential information or individual location information will become a focus of attention.
From the features above and the deep understanding of the user needs, ICT can be labeled by “M”, that is M-ICT. The profound connotation of “M” includes man-man, man-machine, machine-machine, and mobile interconnections. Hence, the M-ICT era is also known as the era of mobile internet of everything (IoE).
M-ICT: Solving Key Industrial Problems
ZTE aims to be an enabler in the M-ICT era and create value with information. This is also the company’s M-ICT strategy. ZTE seeks to create more value in each link of the information flow, i.e., help customers gain more value in each link of collection, distribution, processing, storage, transmission and consumption.
ZTE has chosen the M-ICT strategy to convey its strong determination towards innovation and transformation. In the next three to six years, ZTE will spare no effort in innovating, transforming, and building core M-ICT competitiveness, and leading into the M-ICT era. The M-ICT strategy is devised to solve key industrial problems and help customers create value.
● For operators: ZTE collaborates with operators to increase their pipe capacity and make their pipes more intelligent and flexible. By understanding the role of pipes in information society and through data mining engine, the M-ICT strategy helps operators explore the multidimensional value of traffic forward, backward and acceleration operations to increase user stickiness. By using an innovative identifier network (IDN), the M-ICT strategy can expand the 4G network from public service to government-enterprise customer service and change a centralized network into a distributed network. This helps create a distributed business model, expand user base, and increase revenue. The M-ICT strategy also significantly reduces O&M costs through software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV).
● For government and enterprise customers: The M-ICT strategy provides ubiquitous IT services for governments and enterprises, reduces costs, and improves operational efficiency. It can deploy easy and secure mobile office rapidly to improve work efficiency through integrated end-to-end solutions such as micro office and super MOA. It expands internet of things (IoT) and internet of services (IoS) through machine-to-machine, man-to-machine, and machine-to-service connections. It also helps governments and enterprises optimize service flows and provide better services by building smart cities and enterprises.
● For consumers: With new smart terminals and innovative apps, the M-ICT strategy helps the consumer enjoy ubiquitous services. Life will be smarter, more comfortable, and more colorful, and this enhances consumer satisfaction from access to information, entertainment, and health care.
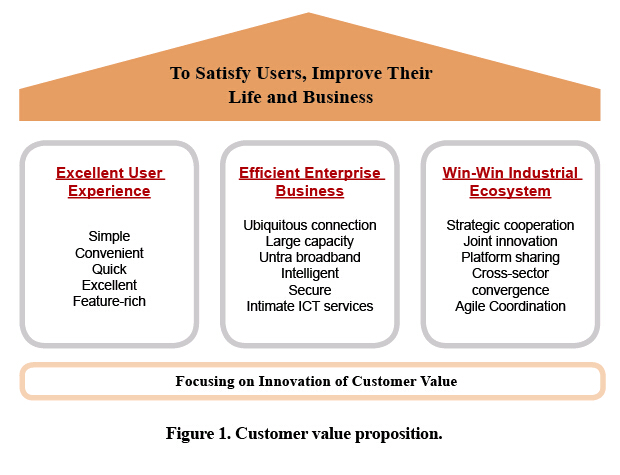
The core customer value proposition of the M-ICT strategy is shown in Fig. 1.
M-ICT: Leading Future Industry Trends
With emerging new technologies and accelerated industry transformation, mobile and IoE technologies are sweeping the industry. The technological and industrial trends in the M-ICT era are as follows.
- Easy Access to High-Speed Services
With the development of smartphones and tablets and the emergence of wireless technologies that solve the last mile access issue, wired broadband access is still around and is evolving to provide wireless access points. In office, home, roadway, airport, high-speed rail, and airline scenarios, 3G, 4G, Pre5G, 5G, and WLAN integrated wireless access mode will provide users with flexible, reliable, and seamless wireless access over the next few years and will develop to offer higher-speed broadband. - The Inevitability of Cloud Intelligent Networks
Smart mobile terminals and cloud applications have driven the growth of data. This has placed enormous pressure on operator networks: demand for bandwidth is up yet revenue is declining. SDN and NFV are gradually being put into practical use. Network convergence, software-definition, cloud, virtualization, and intelligence are becoming a dominant force leading a new round of network innovation. Cloud radio, magic radio, cloud EPC, optical and packet network convergence, SDN, cloud storage, intelligent terminals, and cloud applications will become the secrets for operators and government-enterprise customers to significantly lower their capex and opex. - Big Data Analysis for Value Creation
Big data analysis applications are characterized by volume, variety, value, and velocity (4Vs). They can provide user-centric maps of relationship, intention, consumption, interest and mobility and have increasingly penetrated our daily lives. Big data applications will develop from data to information, from information to knowledge, and from knowledge to intelligence. Information will become increasingly more valuable. Big data will also be applied in fields as diverse as internet, telecom, smart city, smart transportation, smart agriculture, and finance. - Fast-Growing Enterprise Mobile Applications
The rapid development of wireless broadband access and smart terminals facilitates mobile office. With ubiquitous broadband networks and evolving security and IoT technologies, a successful enterprise may launch major external services and inner core applications that cover all aspects of business management and operation and comply with key features of the M-ICT era. This will improve the operation efficiency of modern enterprises, drive the growth of society, and create blue ocean opportunities within the mobile internet market for ICT companies. - Integration of Physical and Virtual Digital Worlds
The physical and digital worlds are linked through information. The value chain and production elements in industries such as office, retail, healthcare, education, entertainment, transportation and SNS will enter the mobile internet industry. A physical map built on the internet will integrate the digital and physical worlds. All the devices in the physical world will be virtually mapped onto the internet. Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies will be used to enable natural experience and interactions between people and things, people and people, and things and things. - Distributed Power Grid and Smart Charger: Making the World Greener
Environmental protection is a dominant theme in society. New energy technologies such as solar energy and hybrid automobile technologies have developed rapidly and will be used more and more in daily life. The electricity converted from solar energy can be connected to the power grid for the benefit of society. Ubiquitous parking systems and wireless charging technology will allow electric buses and automobiles to be charged easily and conveniently. All this will make a better life and a greener world. - Industry 4.0: Evolving from Concept to Reality
The steam engine drove the first industrial revolution; the second industrial revolution saw electricity replace steam as the main source of power; and the third industrial revolution was closely associated with information technologies. However, mobile internet of everything (M-ICT) will ignite the industrial internet revolution. Machine-to-machine, man-to-machine, and machine-to-service connections will allow the number of subscribers to grow exponentially. IoT and IoS will make products, machines, resources, and people connected organically with each other. A smart decision-making service platform that can integrate sensor networks, GPS, cloud computing, and big data will be applied. - Network Security: A Long-Term Technical and Social Focus
The virtual internet community is characterized by concealment, rapid expansion, openness, and interaction and is thus prone to online fraud and other security issues. For point-to-point transmission, information about personal privacy and financial assets can also be easily leaked through social and e-commerce tools on mobile phones. The next-generation network architecture will be identifiable, controllable and traceable and will provide complete trust and identity management. Based on secure chipsets and operating systems, a complete network system with security guarantee will be built by reinforcing safety equipment and service applications.