The Art of Maximizing Revenue from Data
 Tablets and smartphones have fundamentally changed the way people use telecommunications services. Today, service providers are no longer the main creators of value and are under siege from OTT players. At the same time, smartphones have vastly improved the web surfing experience, and this has led to an increased consumption of media and content-based services.
Tablets and smartphones have fundamentally changed the way people use telecommunications services. Today, service providers are no longer the main creators of value and are under siege from OTT players. At the same time, smartphones have vastly improved the web surfing experience, and this has led to an increased consumption of media and content-based services.
In the industrial age, the stream engine overcame human physical limitations. Similarly, in the information age, computers have overcome human mental limitations. At present, we are in the age of convergence, that is, fixed-mobile convergence (FMC), tri-network convergence, and ICT convergence.
Over the past 20 years, telecommunication convergence has implied the convergence of fixed and mobile networks; tri-network convergence has implied the convergence of telecommunication networks, cable TV, and internet; and ICT convergence has implied convergence brought about by cloud computing. Over the next 20 years, convergence in the ICT industry will not only be thought of internally, in terms of network convergence, but also in terms of deeper penetration of ICT into public services, industry, agriculture, education, medicine, and transportation. Such convergence will reform every aspect of individual, family, and work of life. The digital and physical worlds will be brought closer together, and ICT will reach a new peak.
Network evolution over the past 20 years has gone hand in hand with the evolution of smartphones and tablets to cause a significant increase in the amount of data and bandwidth consumed. The inability to handle high volumes of data with limited network resources has been a major problem for every operator and service provider. According to the research by Heavy Reading, by 2020 there will be more than 60 billion devices that will connect every facet of human existence. This will come at a cost for operators, enabling more transactions, data usage, and network events. Operators will have to handle these cheaply and efficiently.
During convergence, operators provide the information flow. From 2G and 3G to LTE, operators seek to improve network quality and throughput, provide numerous value-added services, and improve QoS. Through constant investment in their networks, they expect to increase their customer base and revenue.
In recent years, service providers have also been trying their best to keep up with rapidly changing requirements brought about by mobile internet. The following are the main topics of interest to operators and service providers:
● changing trends in voice. Traffic has been changing from voice to data. Previously, voice was the predominant means of communication, but now there are so many other options. OTT players in the telecommunication industry have largely been responsible for this trend.
● short messaging services. There have been no significant improvements in SMS since it emerged. Smartphones create opportunities for terminal providers and third-party software developers to better integrate phone address lists with SMS and win over users through better experience. The prices of SMS must also be kept low for survival.
● data revenue versus data access. Data access accounts for an increasing proportion of the revenue of mobile communications service providers (CSPs). However, in the mobile industry as a whole, data access accounts for a decreasing proportion of overall revenue. These contradicting trends mean that mobile CSPs are gradually marginalized in mobile internet industry. Mobile CSPs that increasingly rely on data access revenue are considered “pipe liners.”
● growth in M2M business models. With the boom in IP-based wireless broadband networks, M2M services have become a factor that CSPs cannot ignore. Rapid service growth continues to force operators to reassess their business models and provide bundled M2M services. Operators are having a hard time keeping up with dynamic M2M services. Connected, readily discoverable devices have helped change user behaviors over the past few years and will continue to do so in the coming years. This means we will see a further (huge) increase in data transactions and traffic.
● devices connected in a home network. Home networking enables internet content to be delivered to multiple devices within a home. SOHO is an example of a home network.
Essentially, these points refer to a transformation from a homogenized approach to meeting communication and information requirements to a more individualized approach. A good network by itself does not provide sufficient services; a network also needs to come packaged with content and information. Much effort has been expended on improving transmission efficiency and quality in telecommunications networks. However, the internet and new user behaviors have become the new focus of development within the industry. CSPs really need to transform themselves into information providers in order to overcome current predicament.
CSPs need to adopt three strategies:
1. strengthen pipeline infrastructure, such as online charging system and policy manager, to serve both customers and suppliers. This is the basis of business support.
2. focus on user experience (smart care data mall) so that the creators of information continue to use the CSP platform. This could entail providing an app for smartphones and tablets.
3. strongly create platform value to search business innovation (partner relationship management).
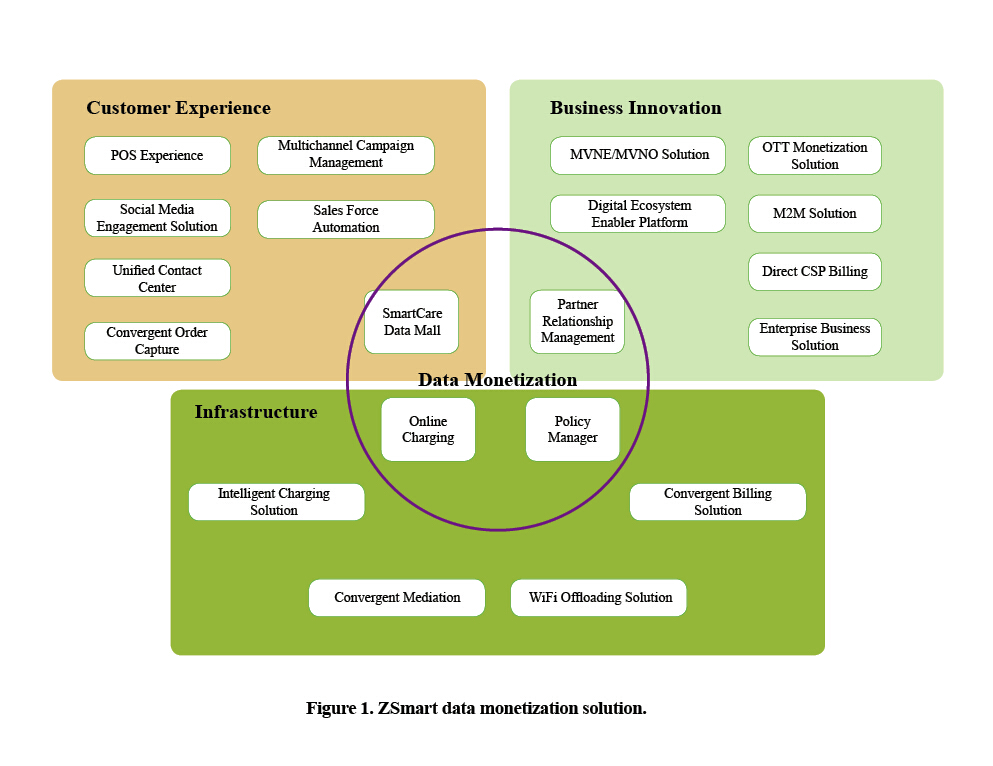
ZSmart data monetization solution helps an operator strengthen its relationships with partners by keeping in mind all important modes, such as “sell with” and “sell to.” This makes operators business enablers. The solution enables efficient charging and policy management and provides the subscribers with an app, such as data mall that tells them about hot marketing strategies.
ZSmart data monetization solution is a typical application of ZSmart BSS in the big-data era. With the three strategies employed by ZSmart BSS, the solution can be used to construct intelligent pipelines. The solution introduces a converged policy and charging solution and encourages customer loyalty through a data mall, which is an application that can be installed on mobile terminals. Finally, a partnership can be formed with OTTs and other manufacturers through PRM as a way of dealing with competitors from the same industry.