Intelligent E-OTN 2.0: Building Smart Highways in Digital and Computing Era
Digital economy has become the key word in national competition and government reports, and is also an important assessment of a country’s comprehensive strength. According to a report by CAICT, the trillion-dollar infrastructure investment bill signed by US president Biden actively promoted network coverage in remote rural areas and improved digital divide. The bill has become the largest investment of the United States in decades. The Korean government has proposed to develop the 5G ecosystem, and plans to increase the number of new 5G firms by nearly 20 times in the next five years, from 94 at present to 1,800. It has also formulated a “6G R&D Initiative” to develop core 6G technologies, with the goal of putting 6G into commercialization in 2028–2030, providing a network 50 times faster than the current one, and expanding the coverage to 10 km above the ground. The European Commission has put forward a Digital Decade Guide that by 2030 all European users will enjoy gigabit broadband connections and 5G networks will cover the whole of Europe. China has made the digital transformation an important measure of the strategy of cyber power, digital China, and smart society, and successively put forward major policy guidelines such as “new infrastructure”, “vigorously boosting the development of industrial digitization”, and “east-data-west-computing” projects at important meetings to promote the digital transformation and digital economy growth.
It is necessary to build a new type of digital infrastructure with the integration of “computing power + ICT network” in the digital era. Computing is the core productivity of the digital economy and also a core driving force after heat and electric power, while ICT network infrastructure is closely related to computing. The countries with high computing power often take the lead in their network infrastructure. As the cornerstone of ICT network, optical network needs to be upgraded and evolved to provide powerful computing. Therefore, ZTE has launched a new intelligent Ethernet over OTN (E-OTN) 2.0 solution that uses DC as the center, has the ability to transport fixed, wireless, cloud/computing and enterprise network services, and features large bandwidth, low latency, flexible scheduling, and intelligent and simple O&M. Its core value is to build extremely high-speed, ultra-broadband transport pipes based on new algorithms, implement agile transport upon the new platform to meet various service-level agreement (SLA) requirements, and adopt new intelligence to create a convenient, intelligent digital all-optical network that ensures high computing power in the digital and computing era.
New Flex Shaping Algorithm: Building Extremely High-Speed, Ultra-Broadband Transport Pipes
According to the latest ICP data center network optical components forecast by Omdia, 400G client interfaces account for 15% of the total in 2022 and are expected to hit about 56% in 2026. As the shipment of high-rate interfaces continues to grow, single-wavelength 400G is bound to be a necessity for backbone and metro optical networks. At the same time, the future traffic will continue to increase, and optical networks urgently need to find other ways to expand capacity if the spectral efficiency remains unchanged.
An ultra-broadband optical network is built in two ways. The first one is to increase single-wavelength rate and transmission distance, that is, maximize spectral efficiency while guaranteeing performance. Therefore, chip and algorithm are quite crucial. At present, ZTE’s OTN system supports single-wavelength 800G and can be upgraded to 1.2T for 400G backbone long-haul (LH) transmission and 1.2T for data center interconnect (DCI). The new Flex Shaping algorithm uses the joint design of electrical domain shaping (Fig. 1) and ZTE’s patented optical domain shaping (Fig. 2) to transmit data longer and pass through more ROADM sites, thus reducing the number of regenerators and Capex. ZTE has repeatedly set records for beyond-100G optical network transport. It unveiled world’s first 1.2T system prototype in 2021, and worked with China Mobile to completed the industry’s first single-wavelength 400G QPSK LH transmission prototype test based on the existing network scenario in July 2022. This test employed G.652 fibers and RAMAN amplifiers for several spans to achieve 49-span 3,038-km transmission without electrical regenerator. This proves the advantage of 400G QPSK in long-distance transmission over the optical backbone network. With the patented optical domain balancing technology, ZTE helped Thailand deploy the world’s first LH Flexgrid 200G backbone WDM network, which increased transport capacity while reducing regenerator boards and Capex.
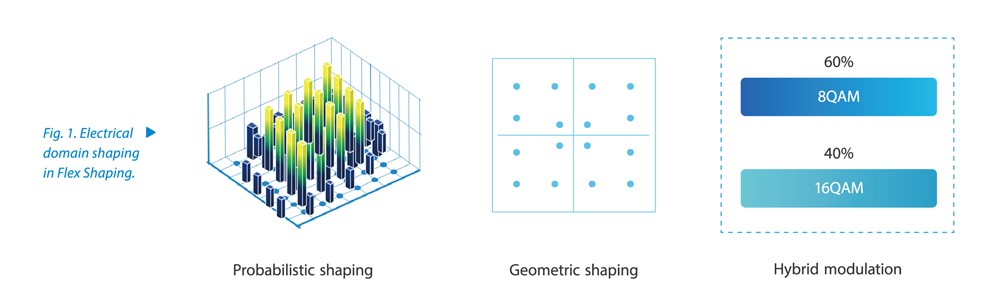
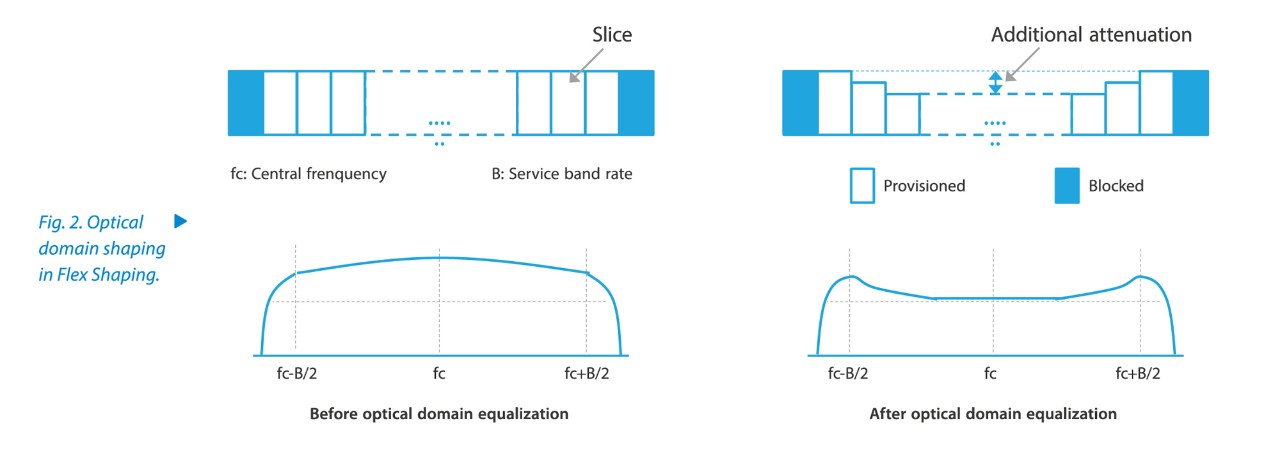
The second way is to expand spectrum width in the optical fiber. C++ band has been widely used and will be extended to L band to double the capacity. Spectrum extension involves many system components. In addition to the new series of traffic boards, new optical amplifiers (OAs) and reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer/optical cross-connect (ROADM/OXC) are also required. At present, the C+L band 11 THz spectrum solution has become mature, and the 12 THz spectrum solution still needs to further optimize OA performance. ZTE has trialed the innovation in this field. It exclusively completed the innovation test of China Mobile’s C+L 11 THz band 400G network in the fourth quarter of 2021, and worked with Turkcell to deploy the world’s first commercial 12 THz ready WDM system in Bursa, the fourth largest city in Turkey in 2022. The evolution to ultra-wide optical network ensures a strong demand for transmission in the digital and computing era.
New Optical-Electrical Synergy Platform: Implementing Agile Transport
The transformation of industrial digitalization has led to a variety of new SLA needs. 4K and XR videos need large bandwidth and low latency, remote industrial control needs millisecond-level latency and ultra-high reliability, and smart home and smart grid need mass connections and low-frequency small-data transport. Everything to cloud needs full-mesh, fast connection and diverse SLAs. All-optical cross-connect platforms, ultra-large-capacity OTN electrical cross-connect platforms, and ubiquitous access capabilities are therefore necessary for full-service optical networks to transport mass data everywhere.
ZTE’s backplane-based OXC system supports 32-degree optical grooming that can evolve to 40+ degrees in the future, allows for multidimensional, cloud-based, full-mesh connection, optical one-hop connection, and guarantees latency-
sensitive services. Without the need to manually connect internal fibers, the all-optical backplane effectively avoids misconnection and cuts the deployment time from week to hour. Compared with traditional ROADM boards, OXC boards integrate OA, monitoring and protection functions, save the footprint by 80% at most and lower the power consumption by 70%. Up to now, ZTE’s OXC solution has served more than 50 optical networks, satisfying the needs of flexible and fast grooming of massive services.
In terms of new ultra-large-capacity electrical switching platform, ZTE is the first to commercialize the single 64T subrack that will evolve to 100T+ in the future. The 64T subrack also supports hitless bandwidth adjustment from 2 Mbps to 100 Gbps and diverse SLAs on demand to better ensure non-blocking add/drop of large DC services. The new platform is backed by core in-house chips such as framer, switching, network processor (NP), and silicon photonic components (SiPh). Relying on ZTE’s in-house third-generation framer integrated fabric interface chip (FIC), the platform reduces overall power consumption by over 50% compared with industry separation mode. The cost-effective Omni-OTN solution supports “5-in-1” unified access to 4G, 5G, home broadband, enterprise network and cloud services, achieving omni-scenario cost-effective transport, omni-area large-capacity coverage and omni-service high-quality access. According to the latest data released by Omdia in August 2022, ZTE ranked No.2 in global OTN switching market.
New Intelligent Operation: Creating a Convenient, Intelligent Digital All-Optical Network
A variety of new digital scenarios are emerging with different requirements. The optical network continues to extend and covers more widely, which makes O&M more complex and evolve to intelligence. The optical network has experienced a long evolution from full manual mode, semi-automation, full automation to intelligence.
Optical network intelligence is reflected in three aspects. The first is network digitalization and intelligence for itself, including rich data collection points based on photoelectric tags, on-demand adjustment of the rate and power of optical and electrical layers based on flexible and agile architecture design, and accurate fault location and risks/demand prediction based on hardware and AI algorithms. The second is intelligence of user experience. Quality services are guaranteed by adjustable, visible and optional capabilities such as diverse SLA services, latency, software/hardware bandwidth and reliability. The third is intelligence of the management and control system. Terminals, edges, networks and clouds can be operated and maintained uniformly via standard and open interfaces. Optical-cloud integration is not achieved overnight, but a gradual evolution from optical network integration, and IP and optical synergy, to optical-cloud integration.
So far, ZTE’s intelligent management and control solution has served more than 100 networks worldwide, including the full deployment of China intelligent management and control systems in 27 provinces, the world’s largest 100G/200G backbone SDON system in China, and the largest 200G intelligent SDON in South America. The solution has greatly enhanced the convenience and intelligence of network O&M.
ZTE has deployed over 600 100G/Beyond-100G OTN networks worldwide in cooperation with global mainstream operators such as China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, Telefonica, VEON, MTN, Thailand’s True, Vietnam’s Viettel and India’s Vi. It will continue to invest in the research and development of optical network technology and work closely with global operators and industry partners to build new intelligent optical networks characterized by ultra broadband, high-quality transport and intelligent operations, so as to meet the need of digitization and computing and create a bright future for human society.