Transport Network Simulation: A Key to Network Quality Improvement
As a 5G network is large and complex, it is of great value to identify and optimize the potential failure risk in advance to improve the quality of the network. Network simulation is to simulate the actual network, restore real network topology and protocols, and build a virtual network. It studies network operation rules and response mechanisms in virtual network scenarios, analyzes the change of network processing capability and network quality under normal and abnormal situations, and thus evaluate the impact of network adjustments on the existing network. This provides decision-making basis for network planning, construction, maintenance and optimization. Network optimization is implemented based on the results of several sand table deductions, which avoids frequent adjustments and improves network O&M efficiency while ensuring network stability.
ZTE's transport network simulation solution involves IP/IPRAN, PTN/SPN and OTN scenarios, and provides various simulation types such as fault simulation, traffic simulation, quality simulation and protocol simulation. A typical network simulation process is generally divided into three steps (Fig. 1):
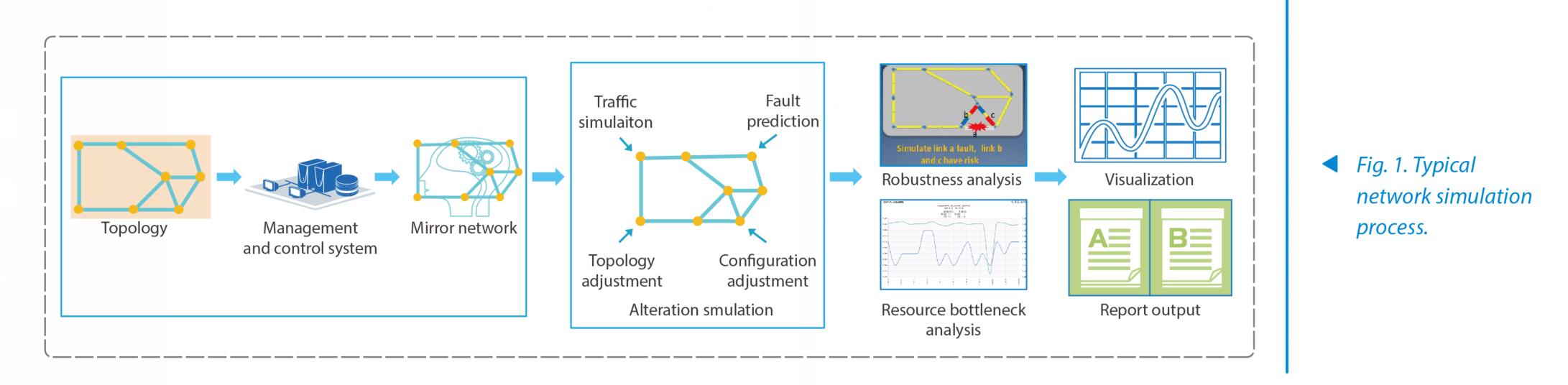
—Alteration simulation: Make various alterations under the mirror network, simulate the alterations in the internal and external environment that may occur in the real network, and output the results.
—Simulation analysis: Analyze the impact of various alterations to the network based on the simulation results, identify risk points and levels, and display them visually to help O&M personnel make the best decision.
Network simulation uses the evaluation method of hypothesis analysis that allows O&M personnel to have a clearer understanding of the fault scope, traffic change, and network quality, so it has wide application value and commercial prospects.
Mirror Network
The mirror network provides a simulation network that synchronizes current network status in real-time for simulation operations, which makes the simulation more real and achieves the effect of online simulation and real-time simulation. According to the requirements of simulation operations, the mirror network consists of three parts:
—Physical pipe, that is, the basic physical network composed of equipment and links, based on which all other work is carried out.
—Logical pipe, that is, dynamic or static paths divided by various tunnel, VPN or routing technologies on the basis of physical pipes.
—Traffic mirroring, that is, to simulate the flow law of data in the logical pipes based on physical and logical pipe models. It helps to build a complete network simulation test environment.
Network simulation is based on the corresponding traffic mirroring. Studying the traffic alteration trend is also the main goal of network simulation.
Alteration Simulation
After the construction, a mirror network simulates network alterations by triggering events around its three basic features (physical pipe, logical pipe, and traffic mirroring), that is, to carry out the simulation operation. Network alterations include fault simulation, traffic or quality simulation, physical pipe simulation (physical topology planning), and logical pipe simulation (protocol simulation).
Fault simulation refers to the simulation of the situation after one or more faults occur in the network, such as IP network L3 link or TE tunnel failure, board or chip fault, and OTN link disconnection. Based on the results of network self-adjustment, it analyzes changes of traffic distribution and network quality deterioration before and after a fault occurs.
Traffic or quality simulation aims to simulate network traffic alterations caused by external or expected traffic events, and to add them to traffic mirroring. By observing the forwarding distribution and changes of network traffic, it can find the possibility, time, and location of network congestion. Moreover, network quality indexes such as delay and jitter are simulated and altered to analyze network quality.
Physical pipe simulation is to simulate physical topology alterations such as capacity expansion or shrink to trigger the change simulation calculation. Based on the results processed by the network itself such as tunnel and service path changes, it analyzes the changes to network traffic or quality.
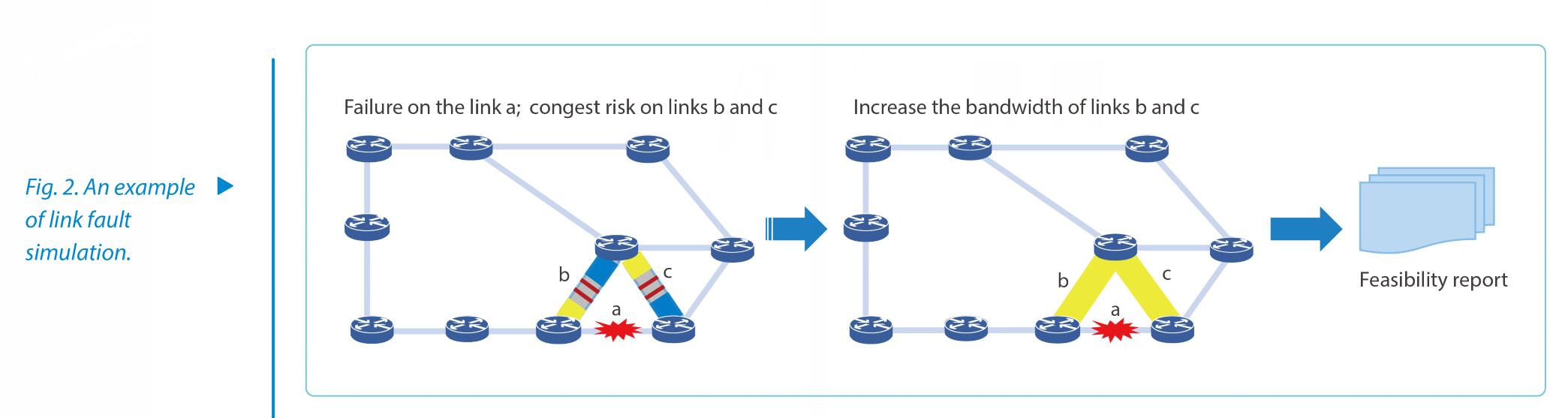
Logical pipe simulation does not change physical topology of the network, but adjusts the device protocol parameters such as bandwidth, protection path, and priority to affect traffic forwarding rules. Based on the results processed by the network itself, it analyzes the changes to network traffic or quality before and after the protocol alteration. The link fault simulation is illustrated in Fig. 2. In a mirror network, the SDN management and control (M&C) system finds that when the simulation link a fails, simulation links b and c will have the congestion risk. Therefore, the system will output a feasibility report and suggest that users should increase the bandwidth of links b and c to avoid potential risks. The network is optimized in advance to improve reliability when it is normal.
Simulation Analysis
The purpose of simulation is to improve network quality and make the network better serve users. It is therefore of great value to judge the results of simulation alternations, analyze the impact of the alternations to local or global network, analyze existing network traffic or quality bottlenecks, and provide guidance for network optimization.
The impact of network alterations can be analyzed from the service level, tunnel level, link level, and network level. At the service level, alternations to the network may trigger rerouting and other actions, thus affecting L2VPN and L3VPN services. Therefore, simulation analysis at the service level focuses on the alternations to service state, service path, service tunnel attached, and traffic flow. Similarly, simulation analysis at the tunnel level involves the changes in tunnel state, tunnel path, tunnel services, and tunnel flow. The impact of alterations on the link level is reflected in the changes of total traffic. The simulation module can judge the network bottleneck by analyzing the accumulative value of tunnel traffic overlapped on physical link. Simulation analysis at the network level evaluates the quality of the whole network. Global network quality indicators (NQI) or customized NQI are established to analyze the impact of network simulation on the whole network. Survivability analysis (robustness analysis) is another method of simulation analysis that studies the anti-attack capability of the network, that is, evaluates the quality of the simulated network in the case of primary failure, secondary failure or even multiple failures. The survivability analysis can also be used to find out the nodes and links that exceed the threshold, so that potential risks can be rapidly located.
Whether it is the analysis of simulation alternations at the service, tunnel, link and network levels or the survivability analysis, the purpose of simulation analysis is to help customers understand the overall quality of the network in a more rapid, intuitive and convenient manner and to give optimization suggestions to help with O&M and improve O&M efficiency.
ZTE's simulation module integrated in ZENIC ONE (ZTE SDN M&C system) has the characteristics of global network simulation and visualization and can support full coverage of 4G and 5G transport network scenarios such as IP/IPRAN, PTN/SPN, and OTN as well as online simulation of tens of thousands of physical network elements. ZTE's transport network simulation solution has been verified in China Unicom, TRUE, and other global markets, helping operators worldwide improve their network quality and O&M efficiency.