5G Boosts Innovation in Video Applications
With the development of 5G networks, video serving as the most representative 5G eMBB service will bring about great changes. More innovative service applications have emerged, bringing brand-new visual experience and business value to individual and industry users. With the continuous development, video will be the first to be commercially promoted on large scale in the 5G era.
5G Live TV
Live broadcast in a stadium refers to a scenario where live sports videos are distributed to on-site audience. At present, most live activities such as sports events are only broadcast to the audience outside the venue, and most of them are presented synchronously on large electronic screens in the venue. Japan took the lead to trial live broadcast to on-site audience at baseball games based on 3G networks, while the United States and Belgium had the live broadcast attempts at the Super Bowl and road cycling races based on 4G/LTE networks respectively.
Because of limitations on network conditions, video latency and business model, the video distribution solutions inside the venue were not really mature for commercial use. But now, with the construction of 5G networks, the technological development in the wireless and video fields, and the approach of the Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games and the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympic Games, innovative 5G live broadcast inside and outside the venues has once again attracted attention. Whether 5G venues create a new B2B2C business model has also become a hot topic.
ZTE's 5G Live TV solution provides the on-site audience with a live event APP on mobile clients such as smartphones or PADs, so that they can watch the live broadcast of the game from any angle of view. Also, by simply zooming or dragging the playback window, they can zoom in or out any part of the video or view the panoramic or wide-angle video in all directions (Fig. 1).
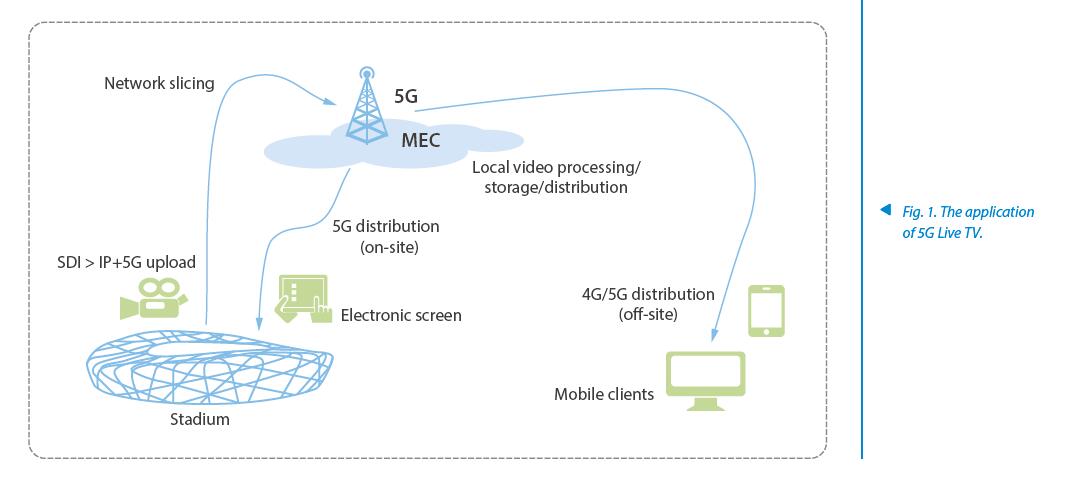
MEC collects and analyzes information about the wireless network in real time, and rapidly and dynamically optimizes services based on the information. In addition to live video broadcast, the stadium can also use this infrastructure to run security sensors and cameras. With the solution to offload video traffic locally, video data from the monitoring devices can be directly transmitted to the data center for local analysis and higher-level decision making.
Cloud VR
VR is recognized as a killer service in the 5G era, so operators in South Korea have launched a large number of VR service applications for 5G commercial use. However, the traditional implementation of VR services restricts its popularity, such as the high cost of purchasing host and terminal hardware, the lack of rich content distributed on various platforms, and the limitation of device mobility.
The large-scale commercialization of 5G networks gives rise to the emergence of Cloud VR architecture. Cloud VR introduces the concepts and technologies of cloud computing and cloud rendering into VR applications. Through a stable network, audios and videos on the cloud are coded, compressed and GPU rendered, and then output to user terminals. In addition to aggregating multi-party contents and rapidly distributing them to user terminals, the cloud platform also reduces the configuration requirements for terminal devices. While the terminals are lightweight and cost-optimized, the platform improves user experience and provides diverse interactive applications such as VR education, VR gaming and VR social networking.
5G significantly improves the development of Cloud VR. For example, a panoramic 8K VR video requires at least the transmission rate of 100 Mbps without using the slicing encoding technology. The application of 6DoF, spatial and optical field technologies will also considerably increase VR video traffic and storage space. To reduce the pressure on transmission bantdwidth, VR video will inevitably move towards more efficient transmission that involves efficient compression algorithm, polyhedral projection, non-uniform encoding, and FOV display mode.
Cloud VR does not mean to reduce latency. Compared with the traditional VR, its rendering process adds three extra steps: image compression and encoding, network transmission, and image decompression. With the 5G network, the overall latency of Cloud VR is much lower than that in the 4G era, reaching a range that can be accepted by users. Although the latency of service procedure is increased compared to the traditional VR, Cloud VR enables VR applications that require complicated rendering on portable mobile VR terminals at any time, bringing more convenience to users.
5G and Cloud VR also bring a variety of lightweight terminals. At present, the popular HMD separates computing/rendering from display. The computing/rendering part can be completed either in the cloud or on terminal devices such as smartphones, servers or set-top boxes, while VR glasses only need to have the display function and weigh about 100g.
8K UHD
Japan's NHK launched the world's first 8K ultra high-definition (UHD) TV channel "NHK BS8K" in December 2018. UHD Forum fully demonstrated the 8K-based UHD technology at the IBC 2019 in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. China is also making great efforts to develop the UHD industry. For example, Shenzhen Municipal Government has taken the lead in making the action plan for the development of 8K UHD industry from 2019 to 2022.
For the big video industry, 8K is a revolutionary technical innovation that affects the entire video industry chain from content production to terminal playback. At present, HDMI 1.4 is the most-used standard for TVs at home. HDMI 2.0 for 4K has not been widely used, not to mention the HDMI 2.1 standard for 8K which was just released in 2018. The HDMI 2.1 cables available for public sale are extremely rare. With the arrival of 8K, even a TV interface needs to be updated. Therefore, it can be seen that 8K will affect the whole process and the whole industry chain that involves content capture, program production, codecs, interface standards for audio and video devices, content storage and distribution, chips, display, and wireless, wired and transport technologies, or even greatly promote the development and application of AI technologies.
8K and 4K both belong to the UHD field and have the same basic technology. 8K includes resolution, wide color gamut, HDR, high color depth, high frame rate, and surround sound (5.1) or three-dimensional sound (7.1+4). Both 8K and 4K adopt PQ and HLG curves to define HDR. There are two solutions for PQ-based HDR curves: static metadata and dynamic metadata. Dolby Vision is the industry-leading solution that combines both static and dynamic metadata. In terms of high color depth, 4K still uses little 8-bit color depth, while 8K widely uses 10-bit color depth and continues to explore 12-bit color depth. As for wide color gamut, the signal output mode used to be RGB or YCbCr. On this basis, BT2100 adds ICtCp, which can deliver a better display on the big screen.
Although audio seems to have no connection with vision, it is still an indispensable element in UHD. Looking forward to the next generation audio (NGA), the use of AC-4, MEPG-H and 3D Audio will bring the audience an immersive audio experience.
In the 5G Live TV scenario, the application of 8K will deliver more event details to on-site and off-site audiences, and the free viewpoint and VR services based on 8K will also bring better immersive experience. ZTE's Big Video and STB teams are creating the 8K home media center, with the aim to bring home users a viewing experience comparable to that of the venue.
In the 5G era, operators and industries have great expectations for the development of innovative video services and actively drive them to commercialization. ZTE's 5G Live TV solution has been commercially used at the 2nd National Youth Games of China and the 15th World Wushu Championships, where free viewpoint (360-degree view), as the highlight of the solution, is officially commercialized on the client of MIGU Video for consumers. Cloud VR applications have been gradually trialed in some provinces in China, and 8K set-top boxes are expected to be commercially available in 2020. As 5G develops, more and more innovations in video applications will emerge and become mature for commercial use.