Exploring NB-IoT Network to Boost 5G IoT Development

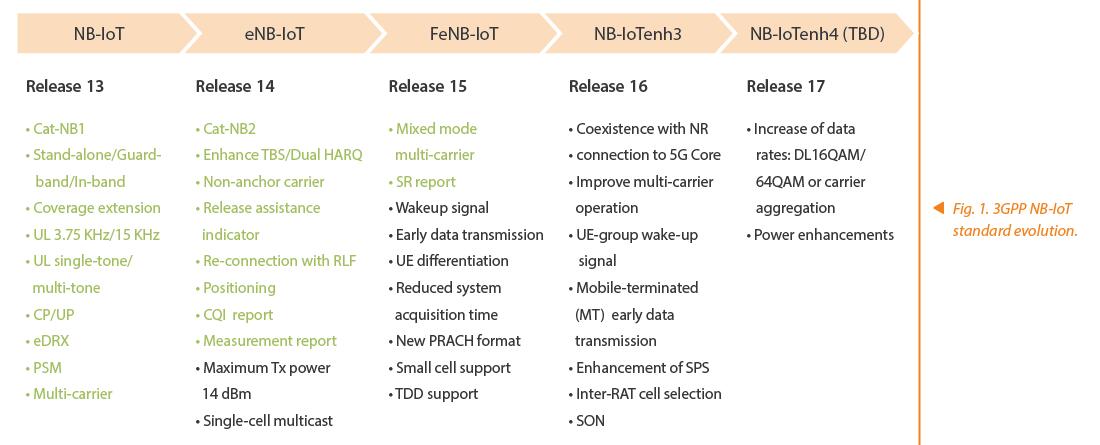
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is a low-power wide-area (LPWA) technology working at the licensed frequency band and widely supported by the world's leading telecom operators and vendors. Compared with other IoT technologies, NB-IoT covers a wider area, consumes less power for its terminals, and has larger number of connections and lower cost. As an important component of candidate 5G technologies, NB-IoT is one of the most important access technologies to meet the requirements of the 5G massive machine type communication (mMTC) scenario. The 3GPP NB-IoT standard evolution (Fig. 1) and the coexistence capability of NB-IoT and NR in the air interface and core network provide important technical guarantee for protecting operators’ investment and ensuring the continuity of diverse LPWA services in the 5G era.
NB-IoT is being implemented at a rapid speed on a global scale with different paces in different regions. By June 2019, the number of commercial NB-IoT networks worldwide had reached 98, and NB-IoT has become one of the most widely used IoT technologies in the world. By the end of 2019, the number of global NB-IoT connection users is expected to exceed 100 million, a combination of GSM based IoT users over the past six years.
NB-IoT industry has a mature and complete ecosystem, ranging from component vendors to terminal manufacturers. Currently, there are 25 Cat-NB1/Cat-NB2 chipsets provided by MKT, Hisilicon, and Qualcomm, and more than 100 modules are ready for commercial use. With the maturity of NB-IoT ecosystem and the number of chips and modules growing at high speeds, the cost of modules gradually decreases to the level of 2G modules. It is expected that the cost will be less than RMB 12 by the end of 2019.
Many operators strongly support and promote the development of NB-IoT. China Mobile has implemented continuous NB-IoT coverage in 346 major urban areas across the country. China Telecom has built 400,000 NB-IoT base stations throughout the network. China Unicom has run commercial NB-IoT trials in dozens of cities across the country, and more than 300 cities have the capability of fast access to NB-IoT.
The support of all kinds of policies opens up a new world for the expansion of NB-IoT. NB-IoT continues to expand the scope of vertical service applications, and the market application scale has developed multi-millions or tens of millions of connection-level services. NB-IoT services have gradually expanded from the smart meter reading, smart manhole covers and smart smoke sensors in early days to today’s shared white household appliances, smart electric vehicles, logistics tracking and smart wearable devices. As the industry chain matures, the development of NB-IoT will evolve from policy-driven to service-driven in the future.
Exploring NB-IoT to Improve IoT Performance
With the prevalence of commercial 5G, IoT technologies have been greatly improved. The NB-IoT network has put forward higher requirements for network performance, which needs to be improved in many aspects such as coverage, user rate, capacity, terminal energy consumption, O&M, and location service.
In-Depth Coverage Solution to Enhance Coverage Performance
The focus of NB-IoT coverage is gradually shifting from wide area to indoor in-depth coverage. Compared with GPRS, by deploying power spectrum density enhancement and repeated transmission, NB-IOT has a coverage gain of 20 dB to effectively improve the penetration ability from outdoor to indoor scenario. However, as there are increasing demands for indoor in-depth coverage, the access requirements of terminals cannot be met only through the enhanced coverage from outdoor macrocells. The indoor distribution system and Qcell solution can be introduced in the wireless network to extend the indoor coverage, and other low-cost in-depth coverage solutions including IoT cells and passive antennas are used for special scenarios such as elevator wells and underground pipeline wells.
User Rate Enhancement to Adapt to More Services
The continuous improvement of single user rate in a NB-IoT network expands new service requirements and enhances user experience. The initial NB-IoT service applications focus on small-packet IoT services such as meter reading and smoke sensor. However, as IoT services extend to white household appliances and wearable devices, the low rate of 3GPP R13 is unable to meet the service requirements. Therefore, 3GPP R14 introduces Cat-NB2 and dual HARQ functions. The maximum uplink rate of a single user is 2.5 times that of R13, and the maximum downlink rate of a single user is 4 times that of R13. In terms of a single user rate, the Cat-NB2 and dual HARQ functions can completely replace GPRS applications. To further improve the single user rate, R17 plans to introduce downlink 16QAM/64QAM and carrier aggregation (CA). Compared with R14, the peak rate of a single user can be increased by six times.
Multi-Carrier Solution to Improve Network Capacity
The expansion of the NB-IoT network from single carrier to multi-carrier can meet the rapid growth of massive terminal demands. Multi-carrier deployment has become an inevitable trend of capacity improvement. Due to random access and paging constraints, the multi-carrier function in 3GPP R13 cannot double cell capacity. After multi-carrier enhancements are introduced, 3GPP R14 can access terminals on non-anchor carriers or send paging messages, so that the cell capacity can be multiplied in a real sense. According to the test results of two-carrier inter-frequency deployment, the overall cell capacity can be increased to three times. 3GPP R15 continues to introduce combination modes such as SA+IB and SA+GB, so that multi-carrier deployment can be expanded to improve network capacity.
Energy Saving Technology to Extend Terminal Life
NB-IoT constantly optimizes the terminal power consumption technology, greatly extending the life of terminal battery. 3GPP R13 introduces eDRX and PSM; R14 introduces release assistance indication (RAI), uplink power control enhancement and 14 dBm terminals; R15 introduces early data transmission (EDT), wake-up signal (WUS) and SR enhancement; and R16 introduces MT-EDT and UE-group WUS. All these help to extend the terminal life and reduce battery replacement.
Intelligent O&M to Improve Network Efficiency
It is an inevitable trend for NB-IoT to evolve from manual O&M to intelligent O&M. Although the NB-IoT service has a short online time and a small amount of data, it has a large number of terminals, a variety of service types and different requirements for network performance. This results in great difficulty in network O&M. Although 3GPP R13 does not support MR reporting at the terminal side, BTS can estimate the downlink NRSRP according to the uplink measurement information, with the deviation between the actual effect and terminal NRSRP not exceeding 2 dB. In R14, MSG3 reports QCI and MSG5 reports RSRP/RSRQ, which can further improve the accuracy of MR reporting. R16 introduces the SON ANR function to implement automatic network optimization. In the future, AI-based intelligent O&M can automatically report problems, locate causes, and optimize networks, and AI will also help the overall resource management based on service types to ensure maximum user satisfaction.
Location Service to Expand Applications
The NB-IoT location service is the basic requirement among other IoT services. Many value-added services can be derived from the location information. Observed time difference of arrival (OTDOA) and enhanced cell identity (E-CID) are introduced to 3GPP R14. However, the field test shows that the positioning accuracy is low (more than 100 meters), which cannot meet the requirement for commercial use. The enhanced solution of E-CID and fingerprint database is therefore introduced, whose positioning precision can reach 50 meters. In some scenarios, the solution can replace GPS to address high power consumption when IoT terminals use the location service.
Great Prospects for Future-Oriented NB-IoT
Evolution of NB-IoT to 5G
As one of the mainstream LPWA technologies, NB-IoT has been evolving to 5G. At the 79th plenary session of 3GPP RAN held in March 2018, 3GPP made it clear that 5G NR mMTC scenario would not involve LPWA in R16, while eMTC/NB-IoT would still be the main application technology in the LPWA scenario. At the ITU-R WP5D#32 meeting in July 2019, NB-IoT was officially recognized as a 5G candidate solution to meet the technical requirements of large-scale mMTC scenarios. This indicates that NB-IoT has the ability of smooth transition to 5G and will continue to evolve as an important scenario standard in the 5G era. This also provides a solid guarantee for future NB-IoT development, allowing operators, equipment vendors, chip manufacturers and vertical industries to be more innovative in technology R&D and business model exploration.
Future-Oriented Development Strategy of NB-IoT
To support co-site deployment of 5G NR, LTE and NB-IoT at the same spectrum, the site co-existence and spectrum sharing are necessary tools to improve spectrum utilization while ensuring existing NB-IoT terminal services are not affected after 5G deployment. If LTE exclusively uses the spectrum resource, NB and LTE co-existence and spectrum sharing are preferred. If the NR and LTE spectrum are fully shared, it is recommended that NB-IoT anchor carrier exclusively occupy one spectrum resource, and non-anchor carrier shall consider sharing the spectrum with NR dynamically.
For future smooth migration from NB-IoT sites to a 5G network, NB-IoT wireless access to 5GC is a problem that must be solved. When combined with the 5G slicing solution, NB-IoT can separate CU and DU to achieve more flexible network deployment. To extend the application in the enterprise or private network market, NB-IoT can combine the 5G MEC solution to realize the localization of enterprise applications.
Conclusion
The arrival of 5G has significantly boosted the development of IoT technologies. The IoT world will be greatly enriched with further 5G commercialization. 5G brings not only faster network speeds but also the possibility of smart internet of everything (IoE). NB-IoT is a pioneer in 5G commercialization. No matter in terms of technology evolution, or global operator network construction, or vertical industrial application, NB-IoT has a good momentum of development that helps 5G explore its way in vertical industries in advance.
It is believed that in the future when 5G will be widely commercialized, NB-IoT as a mainstream candidate technology for 5G mMTC scenario will have a promising prospect in the smart IoE era.