SDN Builds Elastic IP RAN
Large-scale deployment of IP RANs enables operators to carry 2G/3G/LTE mobile backhaul and government and enterprise network services.However, the evolution of mobile internet and customized dedicated lines sets higher demands for packet transport networks in terms of fast cross-domain service provisioning, dynamic bandwidth adjustment, and network capability opening. The vertical and closed architecture of existing networks can hardly meet the service requirements in the ICT era due to difficult upgrade, limited expansion, and inflexible application. The network development trend is open and virtual.
Significance of the Introduction of SDN to IP RANs
With the introduction of software defined network (SDN) to IP RANs, an SDN IPRAN can manage network resources, orchestrate services in a unified way by deploying hierarchical controllers, and implement service innovations by opening northbound application interfaces.
● High efficiency: fast service provisioning. Diverse services and constant changes require IP RANs to respond immediately, so fast delivering fleet and mobile backhaul services is necessary. The introduction of SDN enables network interaction between different vendors and end-to-end service management.
● Intelligence: automatic network optimization. In view of the increasing scissors difference between operators' investment and revenue, and the contradiction between traffic and bandwidth in network planning, how can we predict bandwidth based on service application to optimize network resources in real time? According to data analysis and by virtue of SDN, networks can be automatically optimized to improve bandwidth efficiency.
● Reliability: quick recovery from faults. In an IP RAN, services are provided and managed through manual configuration and the element management system (EMS), which may result in blind areas in fault handling. The dynamic SDN algorithms can quickly recover the network from faults and ensure secure and reliable services.
● Convergence: multi-purpose network. To improve utilization, base station backhaul and fleet services, and home-customer services share the same physical network. How can we turn one physical network into several logical networks? The answer is SDN controllers, which manage and schedule network resources in a unified way, generate multiple logical networks through virtualization, and implement fragmented transmission of various services.
ZTE's SDN IPRAN
ZTE's SDN IPRAN includes APPs, D-controllers, an orchestrator, an H-controller, forwarding-plane devices, EMS, and ZXDNA (Fig. 1).
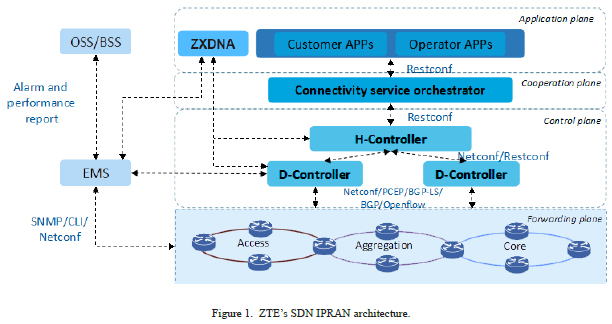
The D-controllers provide services, query topology, and manage and maintain devices in a single domain. With an open architecture, the D-controllers support interoperability of devices from different vendors, and the southbound interfaces support multiple standard protocols. For the IP RAN devices already massively deployed in the existing network, the EMS provides IP RAN network resources to a controller, which orchestrates IP RAN services through data sharing (database) without modifying devices or affecting services.
The H-controller orchestrates and controls services across domains. With the capability of cross-domain topology, resource discovery and management, and cross-path calculation, it optimizes end-to-end paths in the network.
The orchestrator manages end-to-end services, stores service databases and policy databases, and configures service resources.
ZTE's SDN IPRAN has the following features.
Automatic Service Provisioning
ZTE's SDN IPRAN controls and manages IP RANs in a centralized way. The SDN controllers automatically obtain network topology, calculate and select paths, and set up service channels without manually configuring complex IP/MPLS protocols on devices. In addition, one-click deployment of IP RAN services shortens the configuration time by more than 20 minutes. A maintenance window APP is used for service maintenance, reducing the workload of daily maintenance by 80% and increasing the O&M efficiency.
Network Reliability (TE HSB+BGP FRR) and Controller Cluster
In an IP RAN, multiple protection mechanisms are used for service redundancy. ZTE's SDN IPRAN is equipped with TE HSB+BGP FRR protection policies by SDN controllers to improve network reliability.
The SDN integrates the control plane to the controllers whose reliability is therefore vital to the network. With elastic IPSDN controllers and mature cluster components, ZTE’s SDN IPRAN supports: data slicing and load sharing for data consistency, backup and restoration, the active/standby and cluster modes for controller protection and load sharing, and distributed calculation for allocating tasks to different cluster nodes.
BoD
With the constant change in service demands, how to match open, real-time, and on-demand data bearers becomes a major issue for IP RANs. BoD is therefore introduced to address this issue.
BoD is an application developed based on Restful API, a northbound standard. Users manage service bandwidth on the BoD APP interface, such as providing and adjusting online-bandwidth, and customizing the bandwidth calendar.
● Bandwidth provisioning on demand. With the BoD APP, users select ports, service bandwidth, and SLAs from the rented resources, and then services are provided on line.
● Bandwidth adjustment on demand. When the bandwidth demand changes, users directly modify the bandwidth by logging in to the APP and select services as they like.
● Bandwidth calendar customization. Users customize the automatic bandwidth adjustment policy on the BoD APP according to their demands. The bandwidth can be adjusted at a certain time point of a day or from a period of time.
Smooth Evolution from IP RANs to SDN IPRANs
How do the existing IP RANs smoothly evolve into SDN IPRANs is a common concern of operators. To reduce the difficulty of the introduction of SDN and protect the investment of operators, ZTE's SDN IPRAN upgrades smoothly from the existing IP RANs to SDN IPRANs by introducing D-controllers and H-controllers without changing the existing IP RAN hardware. The principle of the upgrade is as follows: the EMS of IP RAN abstracts all IP RAN devices in a unified way, opens network resources and topology to D-controllers through vendor-defined interfaces, and thus controls the existing IP RAN through D-controllers. In view of massive configuration data in the EMS, the upgrade supports the coordination of D-controllers and the EMS.
Significance of ZTE's SDN IPRAN
ZTE's SDN IPRAN achieves hierarchical intelligent control and network capability opening by introducing SDN. Through hierarchical controllers, it deploys, operates, and maintains services in a unified way, and implements services innovations with open northbound application interfaces.
● Improve the efficiency of cross-domain service provisioning. Fleet services are set up and changed in real time, which involves fast service provisioning, bandwidth adjustment, and service migration. The introduction of hierarchical controllers improves efficiency of service provisioning in the cross-domain and cross-vendor scenarios. After users customize services through an APP, the controllers quickly respond to their demands. The duration for service provisioning and adjustment decreases to several minutes, which was previously several months in the existing network. This greatly improves user experience.
● Increase the utilization of network resources. By collecting network resources, the ZXDNA analyzes data and suggests network adjustment. According to the rules, the controllers dynamically adjust network resources.
● Promote O&M efficiency. The centralized control plane provides end-to-end O&M and protection for detecting resources and services in real time. In case of network failure, the controllers can calculate paths to recover services as long as there are physically reachable routes.
● Network virtualization for fragmented-resource sharing. The controllers abstract and fragment network resources. The fragmented network resources form multiple logical networks to independently control the resources for mobile backhaul services, fleet services, and home-customer services, thus facilitating optimized operation and management of network resources.
● Open system for service capability improvement. Restful network programmable interfaces can lead the industry to open model and make networks adapt to quick service launch. This avoids network reconstruction and reduces CAPEX and OPEX.
The Application and Outlook of ZTE's SDN IPRAN
Cooperating with domestic and overseas operators, ZTE has trialed SDN several times in the IP RAN field.
ZTE helped Jiangsu branch of China Telecom in prototype design and pre-commercial trial of the SDN IPRAN, promoting the application of SDN. Moreover, ZTE worked with Jiangsu branch of China Unicom to deploy the SDN IPRAN in Yangzhou and performed loaded tests on 4G LTE voice and data services, reducing the high maintenance costs due to enormous NEs in the IP RAN.
In addition to domestic operators, ZTE cooperated with overseas operators, such as Vodafone, in IP RANs and completed verification tests of SDN PoC, promoting the commercial progress of SDN in the IP RAN field.
In the future, with the expansion of SDN IPRAN trials, the resource optimization, network capacity openness, and O&M simplification brought by the SDN will speed up the commercialization of SDN IPRANs.