1+N Solution Extending 5G from Campus Network to Field Network
Industry is not only the major force of the national economy, but also the foundation of social economic development. In recent years, China has been proactively promoting the integration of 5G and industrial Internet. The 5G industrial Internet has gradually become an important pillar for China's new industrialization.
After years of exploration, ZTE has released the 5G solution called "1 campus network + N field networks" which aims to integrate 5G applications into the domains of manufacturing and operation. This solution supports the construction of 5G fully-connected factories covering campus network, shop-floor network and production-line network, facilitating the expansion of the 5G industrial Internet.
Why We Need the 5G Field Network
Various industries, including steel-making, mining, port, metallurgy, and manufacturing, are actively pursuing digital transformation, guided by the forerunner enterprises. For example, in the steel-making industry, there has been an increase in investments for informatization, digitalization and intelligence with more than 80% of China's steel-making enterprises promoting intelligent manufacturing.
China keeps promoting the transformation of traditional industries, and the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, along with multiple departments, has launched policies such as the 5G Application "Sailing" Action Plan, 5G Industrial Internet Promotion Plan, and 5G Fully-Connected Factory Construction Guide. The aim is to extend the 5G industrial applications from peripheral activities to core production activities and promote the industrial transformation.
5G, as a wireless technology, will be gradually introduced into the production domain. For industry customers, the high performance and wireless features of 5G will fundamentally change their working modes, facilitate elastic production, and unlock potential benefits in multiple aspects such as production capacity, revenue, manpower, and security. Deeper integration of 5G into operation domain will bring greater value for operators and increase user stickiness.
Whether the 5G campus network could fulfill the field applications? Actually, field applications have three unique demands. First, they have extreme requirements for determinism. The existing performance capabilities of the campus network depend on the public network, making it difficult to apply various strict assurance measures. Second, field applications need closed-loop data. That means the generation, receiving and processing of data must be closed-loop on the field to ensure continuity and security. However, the campus network relies on remote public clouds or is closed-loop at the campus level, making it challenging to match local close-loop requirements. Furthermore, some field networks, especially production-line network, need to be pre-integrated by integrators in advance. The campus network serves multiple services and even public subscribers, so it can't match the pre-integration and migration requirements of production lines. Therefore, serving field applications directly using the campus network is difficult. To better serve the manufacturing process, we recommend overlaying field networks on the basis of a 5G campus network, i.e., a"1+N hierarchical 5G private network" (Fig. 1) .
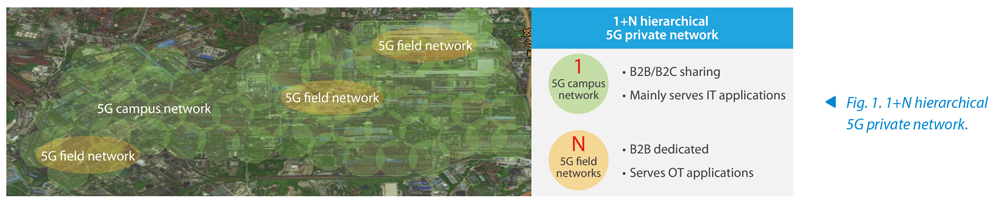
Core Requirements and Challenges of the 5G Field Network
Traditional industrial control networks connect all devices through wired networks, such as industrial Ethernet and field buses, with programmable logic controller (PLC) at the core. However, this presents several challenges for the digital transformation of the industrial control network. First, wired networks are difficult to deploy and prone to failures, which don't allow the production lines to make quick adjustments, resulting in low flexibility and hard service upgrades. Additionally, the traditional PLC ecosystem is closed, and regular upgrades of software and hardware can be costly.
We have implemented 5G digital transformation in many industries. For example, in a steel-making enterprise's crane scenario, 5G is utilized to support wireless PLC northbound connection between the unmanned crane and its control system. This allows convenient deployment of the crane while avoiding many hidden troubles and fault points caused by moving cables. In an automatic logistics sorting scenario, a large-scale automatic control center requires the cooperation of PLCs with thousands of I/O points. By using 5G technology, the master-slave PLC system can be connected wirelessly, greatly simplifying the cable deployment and facilitating the upgrade of the automatic logistics sorting system. Furthermore, in 3C electronics manufacturing where elastic production is a significant requirement, 5G technology can be used to enable wireless PLC southbound connections between the PLC and the end equipment, enabling flexible and elastic production.
After analyzing typical field network scenarios, we've found that using 5G to serve the field applications should be done step by step, and there are three top challenges to be addressed when implementing 5G field networks.
- Difficulty in performance guarantee: With 5G-driven cord-cutting, the deterministic requirements have become higher and higher. For example, the southbound communication of PLC requires ultra-low latency assurance.
- Requirement of cloud, network and applications: Applications are key to digital transformation of industries. How can we easily deploy all kinds of applications? We need to take into account cloud platform and applications besides the 5G network.
- Complex network O&M: Although 5G provides convenience to applications, traditional 5G networks are really complicated for enterprise self-O&M.
Three Core Capabilities for ZTE 5G Field Network
After extensive practice, ZTE has proposed three key capabilities of 5G field network: deterministic guarantee, one-stop cloud-network solution, and simplified O&M for enterprises (Fig. 2).
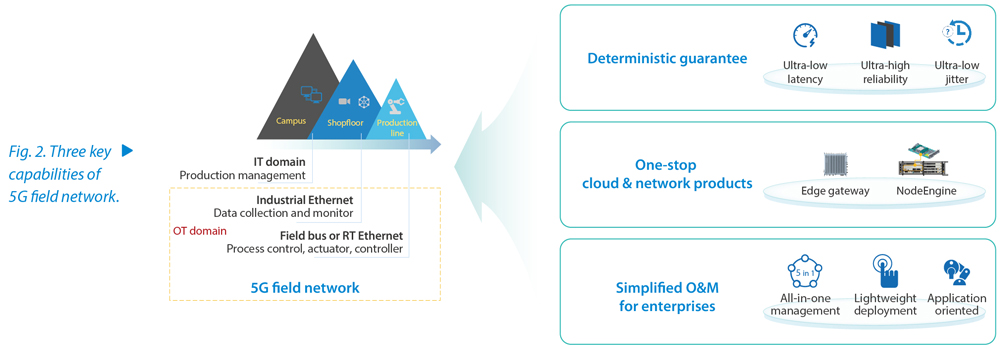
- Deterministic Guarantee
For common applications of 5G field network such as data collection, AGVs and PLC northbound, deterministic requirements of 20 ms@99.99% are typical. To meet these requirements, it is recommended to use network enhancements such as local traffic offloading and frame replication and elimination for reliability (FRER) to improve network capabilities. In addition, features such as short SR period, intelligent pre-scheduling and low MCSs can be introduced to improve the air interface capabilities. To accurately guarantee different applications, precise service identification, scheduling and KPI measurement can be used.
As 5G cord-cutting continues, latency requirements become higher, less than 10 ms@99.999% for applications like PLC southbound, along with strict jitter requirements. For these services, URLLC technology needs to be introduced to provide ultra-low latency and ultra-high reliability, and TSN technology also needs to be introduced to guarantee jitter as low as 1 ms.
- One-Stop Cloud-Network Products
Applications play a key role in the digital and intelligent transformation of industries. To achieve flexible, convenient, and low-cost deployment of various industrial applications, cloudification is currently the trend. That means cloud, network, and industry applications should be taken into consideration during transformation. For this purpose, ZTE provides one-stop cloud-network products for 5G field network, so that computing power can be extended from the campus network to the field network, enabling on-demand deployment of applications. On the edge side, ZTE provides the industry-only site-level computing engine, NodeEngine. By inserting the computing engine board into BBU, ZTE can rapidly upgrade the common base station to the computing base station to implement local traffic offloading and local application deployment. This helps to integrate 5G base stations with industrial applications. On the terminal side, ZTE has launched a series of 5G edge gateways that provide not only abundant interfaces for interconnection with various industrial devices but also built-in computing platforms for applications such as video coding and PLC control.
- Simplified O&M for Enterprises
To reduce the barriers of applying 5G to vertical sectors, ZTE has developed a series of features that greatly simplify O&M for enterprises. These features include an all-in-one management system that provides end-to-end management capabilities across wireless network, core network, bearer network, fixed network, and terminals, and the self-service IDOS portal that enables enterprises to monitor and manage the applications independently.
By working with operators and industry partners, ZTE has gotten rich experience in building 5G fully-connected factory in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, ports and mines. Leveraging its innovative 5G industrial Internet integration capabilities, ZTE will continue to empower the intelligent transformation and upgrade of China's manufacturing industry.