ZTE Virtualized Network Integration Center: Taking the Lead in Digital Integration
Telecom networks have entered the cloud era. Implementing fast and high-quality network functions virtualization (NFV) integration is the primary concern in current NFV network construction. ZTE has independently developed its virtualized network integration center that can help operators standardize, informatize and automate integration delivery, improve the efficiency and quality of NFV network construction, and explore new modes of digital NFV integration.
Construction Goal
ZTE virtualized network integration center achieves asset digitalization, management digitalization, and production digitalization through the introduction of digital means.
- Asset digitalization: The center digitally models the assets in the process of NFV network construction and O&M. Through the asset information management platform, it implements centralized management of asset information, supports asset allocation, analysis and early warning, and improves usage efficiency of the assets.
- Management digitalization: Through the project management platform, the center implements end-to-end task-driven closed-loop management, including task allocation, progress feedback, output archiving, tracking of pending issues and task audit to ensure that the task progress and quality achieve the goal.
- Production digitalization: The center introduces a pipeline to orchestrate production operations. It eliminates tool islands, forms a fully automatic tool chain, and achieves end-to-end fully automated production capabilities of NFV networks ranging from demand input, planning and design, installation and deployment, data configuration, integration testing and service launch.
System Architecture
ZTE virtualized network integration center is a digital management suite that implements end-to-end NFV integration. It covers the lifecycle management of NFV resource pool, including NFV network planning, deployment, configuration, testing, O&M and monitoring.
The capability layer consisting of iCAL, AIC and iDOP supports upper-layer applications (Fig. 1).
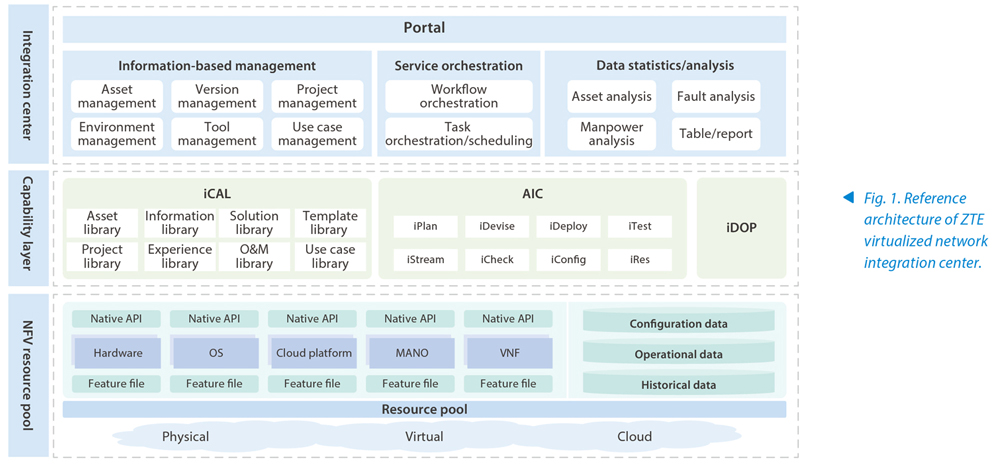
- Integration capability asset library (iCAL): It classifies and manages all objects involved in the NFV network, provides external APIs for access and operation to upper-layer applications, and achieves resource and service sharing.
- Auto integration center (AIC): It provides a series of integration tools such as planning, design, deployment, configuration, testing, and inspection as required in NFV network construction to achieve continuous end-to-end integration and deployment capabilities and improve the efficiency.
- Integration digital operation platform (iDOP): It is an O&M support platform that implements digital management and analysis of NFV networks. Through the iDOP, a large number of NFV networks can be monitored in a centralized manner, which improves O&M efficiency while reducing the costs.
The application layer supported by the capability layer provides common application functions for implementation and management of integration services, including the information management platform, service orchestration, and data statistics and analysis.
The information management platform manages and maintains asset and information libraries, including:
- Asset management: It manages and maintains all hardware and software.
- Project management: It adopts multi-project management mode, and each project is managed and maintained independently without interference.
- Environment management: It builds the test environment by allocating resources from the asset library. The resources are allocated to different projects and returned to the asset library after use.
- Use case management: It manages and maintains use cases and automated scripts they use.
- Tool management: It allocates resources in the resource pool, completes the installation and configuration of the tools, and supports self-developed and third-party tools.
Service orchestration includes task orchestration and workflow orchestration. Task orchestration is to break down the work of project and orchestrate the tasks in accordance with project objectives as well as the procedure and time requirements such as requirement analysis, solution design, environment building and integration test. It creates a list of tasks and assigns the tasks to different recipients who output relevant solution documents or design files as required. Workflow orchestration is to define the workflow in five scenarios such as integration design, deployment, test, acceptance, and management in the process of NFV network construction. Based on the digital means, the integration work within a task is divided into several minimum units that can be executed. These minimum units are cascaded into a complete pipeline through orchestration, so that these units can be periodically executed and output reports in accordance with the predefined scheduling policy. In this way, highly automated continuous integration or continuous deployment tasks can be implemented.
Data statistics and analysis can help enterprises make auxiliary decisions and improve equipment utilization and personnel efficiency through visual charts, statistics and analysis of the asset utilization of all kinds of equipment as well as the occupancy of human resources.
Application Scenarios and Value
The virtualized integration center can help operators improve integration efficiency, reduce the costs, and ensure integration quality during their NFV network construction. Typical application scenarios are as follows:
- Pre-integration verification of multi-vendor devices based on the OpenLab: As NFV network decoupling increases, integration verification of multi-vendor devices has always been a major difficulty in commercial use of NFV networks. Through task orchestration in the virtualized integration center, a complete task flow involving requirement analysis, solution design, environment building, test verification, and document output can be arranged. This helps to implement pre-integration verification among multi-vendor devices.
- CI/CD based on the virtualized integration center: For customized integration scenarios, automatic production operations are orchestrated in advance in the virtualized integration center to implement continuous integration (CI) covering from inspection, deployment, testing to version delivery. In addition, in the commercial environment, after the hardware in the resource pool is installed and connected, the production operation pipeline for commercial deployment can also be orchestrated in the virtualized integration center. For the versions that have been verified in the center, a series of operations in accordance with the CI sequence such as deployment, configuration, and testing of the commercial NFV networks can be completed automatically to implement continuous deployment (CD). This automated continuous verification and deployment workflow can implement version iteration and commercial deployment of NFV networks. Through the effective connection between CI in the test environment and CD in the commercial environment, the efficiency of NFV network integration is significantly improved while reducing the verification cost.
Up to now, ZTE virtualized integration center has been applied in commercial networks around the world, helping operators achieve rapid construction of NFV networks. ZTE will continue to work with operators worldwide to promote further development of virtualized integration services towards digitalization, automation, and intelligence, and lead digital integration to create new business value.