POTN: Making a More Intelligent and Flexible Network
A packet optical transport network (POTN) is a future-proof, integrated transmission technology combining packet and OTN technologies. It enhances the performance of legacy networks, breaks down the barriers between multi-layer networks, reduces network construction and O&M costs, and provides intelligent and flexible integrated service bearers. With the boom in data services, POTN is entering large-scale commercialization.
Challenges Faced by Legacy Networks
With the advent of 4G, Ethernet private line and home broadband services have been ushered into the age of big data. Operators are now facing the following challenges: bandwidth deficiency, network layer optimization, and resource shortage.
The bandwidth required for 3G base stations is tens of megabytes per second, and that for 4G base stations is can be hundreds of megabytes per second. The bandwidth of VIP customer private lines has been upgraded from two to ten megabytes to hundreds or thousands of megabytes per second. Moreover, OLT uplink requires high bandwidth bearers. The bandwidth of the access layer (GE/10GE) and the core convergence layer (10GE/40GE) of the original PTN network in developed cities cannot meet requirements in the big data era. Operators are urgent to upgrade or reform their transport networks in order to provide higher bandwidth.
The existing packet + OTN architecture is restricted in terms of fast service provisioning, network protection, and O&M. Therefore, POTN has become the focus of the industry, as it aims to simplify network layers and develop convergent products.
As the traditional packet + OTN architecture has been extended to the lower layer, various problems have emerged, including high investment cost, large equipment room space, fast resource consumption, and difficult service scheduling. POTN, which simplifies network layers and optimizes transport network resources, is therefore introduced. To address the problem of fiber resource shortage that operators are facing, POTN combines packet and OTN technologies, which leverages the large capacity of OTN and saves fiber resource.
ICT enterprises, including ZTE, are promoting transport and bearer network technologies. POTN is a new packet transmission technology developed in recent years. By combining packet and OTN technologies, POTN increases the ability to bear multiple services, enhances interface capacity and transmission performance on the line side, simplifies the network structure, and saves network construction and O&M costs. Thereby, POTN has become a hot transport network technology in the big data era (Fig. 1).
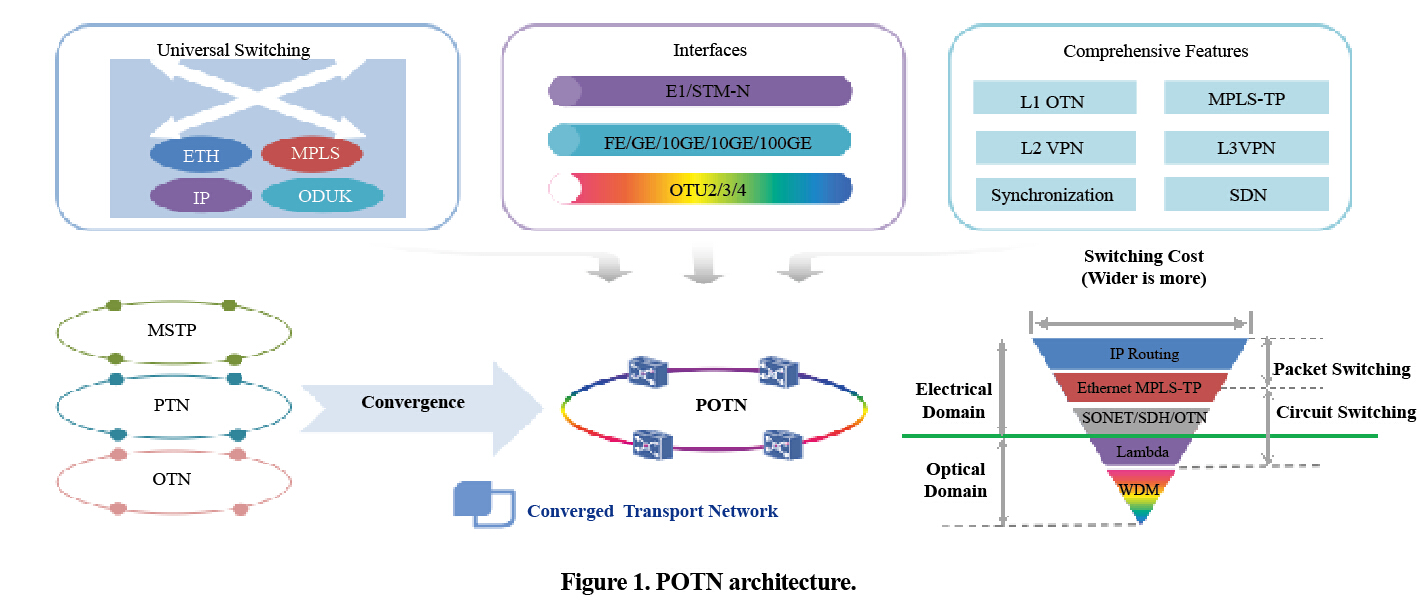
POTN has the following advantages.
High Bandwidth
With the large-scale deployment of 4G, access bandwidth is being increased, and data traffic is growing exponentially. Operators have strong demands for high bandwidth. Currently, the capacity of POTN on the line side has reached 100 GB, and can be expanded to 400 GB with specific technologies. In the future, with technology innovation, POTN will have greater interface abilities to improve network bearing capabilities and meet demands for high bandwidth.
The unified cell switching matrix is the kernel of the forwarding plane for the POTN. The matrix:
● provides various service interfaces, such as packet and OTUk
● completes unified cell exchanges of all packet and ODUk sub-wavelength services
● implements unblocked intersection of services between line cards
● supports hybrid transmission of any proportion of packet and OTUk services.
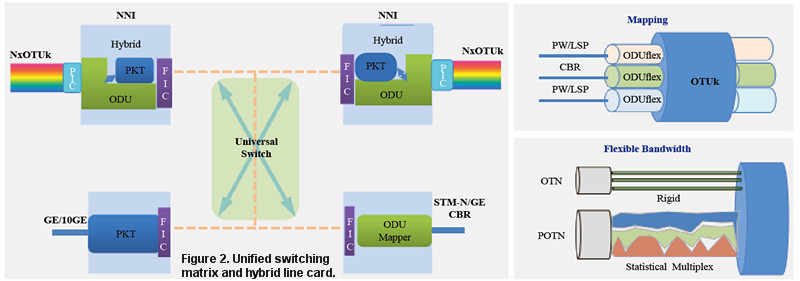
The hybrid board on the line side of the POTN, which transmits colored NxOTUk optical interface signals, combines packet and OTN technologies. Packet services access the universal switch through a packet interface board, and CBR data and traditional STM services implement ODU mapping directly before they are transmitted to the universal switch. Packet services and ODUk sub-wavelength services can be dispatched at the line card on the same hybrid line side, which enables exchanges of any proportion of packet and OTU services (Fig. 2). The PIC module multiplexes signals to OTUk colored optical signals and then outputs the signals. Different services can be transmitted by different ODUflexes so that the ODUflexes are isolated from each other. With the POTN technology, CBR and STM services can be directly mapped to rigid pipelines of the OTN and statistical multiplexing elastic pipelines that are based on packet services.
By combining packet transmission and OTN channel scheduling capabilities, POTN achieves a three-dimensional transport pipeline scheduling system. This can reduce network congestion and improve multi-service bearing capacity and service quality.
By using the SDN-oriented control architecture, POTN achieves separation of control, forwarding and application. It also:
● provides open northbound interfaces to the external devices
● enhances network intelligence with the centralized network management system and controller
● simplifies multi-layer network O&M
● solves problems with devices docking and coordination between multiple vendors.
For hundreds of thousands of pieces of PTN equipment, the evolution can be implemented through centralized network management and control. For newly built equipment, controllers are added for centralized control over standard interfaces. At the upper layer of the centralized network management system and controller, a collaborative layer is added for unified collaboration, therefore achieving the SDN evolution of the entire PTN network.
With the centralized control, the SDN controller can gain the global network topology and status, which facilitates global optimization, and provide end-to-end network deployment, security, and detection. Moreover, the SDN controller can centralize control in multi-layer networks, and implement collaboration and optimization of multi-layer and multi-domain networks. In addition, after being managed and integrated by the centralized SDN controller, network resources can be virtualized. That is, the coarse granularity POTN resources are virtualized into on-demand network fragmentations, so as to provide services to upper-layer applications through standardized interfaces.
POTN interprets a virtualized transport network solution in the SDN era. POTN can be used for trunk bearer, metropolitan mobile backhaul services, metropolitan OLT uplink home broadband services, and metropolitan private line and network services.
In December 2013, ZTE officially launched the first POTN smooth evolution solution. In August 2014, the POTN-based ZXCTN 6500 completed tests during the concentrated purchase of China Mobile and was commercially trialed by Jiangsu Mobile, Shanxi Mobile, Hunan Mobile, and Jiangxi Mobile. In December 2014, POTN was put into commercial use by Suzhou Mobile. In 2014, the POTN-based ZXONE 9700 ranked first in the concentrated purchase of China Telecom for national backbone networks, accounting for 40% of the market share. Major operators have begun the scale deployments of POTN, marking maturity of the POTN technology. During the 2015 Mobile World Congress Shanghai, POTN has gained widespread concern in the industry, and has become an inevitable trend of the transport network evolution.