Application of D2D in 5G Networks
Cellular communication systems have evolved from 1G analog, represented by voice services, to 4G wireless broadband, represented by mobile data, computing, and multimedia. With the prevalence of smart terminals and explosive growth of network traffic, there is a clearer, more pressing need for evolution to 5G mobile technology.
In the evolution to 5G, traditional performance indicators, such as network capacity and spectral efficiency, need to be continually improved, and a wider variety of communication modes and applications need to be provided to enhance user experience. Device-to-device (D2D) technology has drawn widespread attention in the industry for its potential to improve system performance, enhance user experience, and expand cellular applications.
What is D2D?
With cellular-based D2D communication, also called proximity service (ProSe), user data can be directly transmitted between terminals without routing via eNodeBs and core network. D2D communication has a structure quite different from that of a traditional cellular network (Fig. 1).
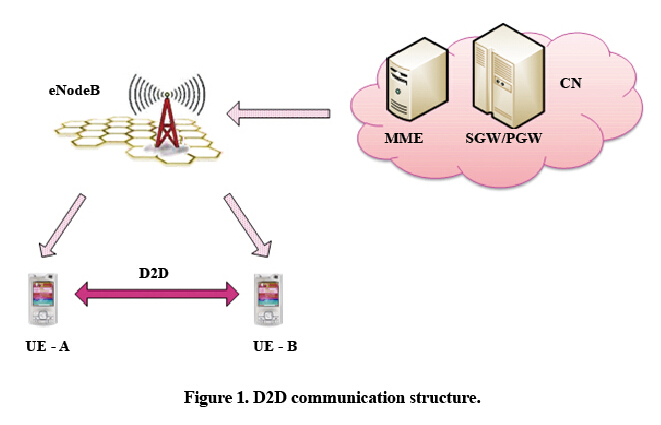
D2D communication helps increase spectral efficiency, enhance user experience, and expand communication applications.
Increasing Spectral Efficiency
In D2D communications, user data is directly transmitted between terminals without routing through a cellular network and thus results in hop gain. Moreover, resources between D2D users and between D2D networks and cellular networks can be reused, and this results in resource reuse gain. With the hop gain and resource reuse gain, wireless spectral efficiency and network throughput can be increased.
Enhancing User Experience
As mobile services and technologies develop, short-distance data sharing between nearby users, small-scale social and commercial activities, and location-based services for local users will become a significant source of business growth on the wireless platform. D2D technology based on nearby user discovery will enhance user experience in these service modes.
Expanding Communication Applications
Traditional wireless networks were demanding on communication infrastructure. The communication system may collapse if core network facilities or access network devices are damaged. However, D2D communication makes it possible for cellular communication terminals to set up ad hoc networks. If the wireless infrastructure is damaged or terminals are not covered by a wireless network, multi-hop D2D can be used for peer-to-peer communication or even access to cellular networks. In this way, the number of wireless applications can be expanded.
Standardization of D2D in the 3GPP LTE system started with LTE Release 12. Unfortunately, D2D discussed in LTE Release 12 only supports broadcast communication and has very limited functions. The potential gains and applications of D2D need to be developed in future 5G networks.
Potential 5G D2D Applications
Applications of 5G D2D include local service, emergency communication, and IoT enhancement.
Local Service
In local service, user data is directly transmitted between terminals and does not route through the network side.
Local service is typically used for social apps. Social apps based on the proximity feature are a basic D2D application. With the D2D discovery and communication functions, a user can find other nearby users and share data or play games with them.
Another basic application of local service is local data transmission. Local data transmission leverages the proximity and direct data transmission features of D2D to expand mobile applications while saving spectrum resources. This creates a new source of revenue for operators. For instance, local advertising service based on proximity can accurately target people to maximize its benefits. A shopping mall can send commercials, discounts and promotions to people who walk into or around the mall, and a cinema can push movie information and showtimes to people nearby.
A third application of local service is cellular traffic offloading. As media services such as HD videos become popular, their massive traffic flows put tremendous pressure on core networks and spectrum resources. D2D-based local media services can help operators save their core network and spectrum resources. In hotspot areas, operators or content providers can deploy media servers that store popular media services. These media servers deliver media services in D2D mode to users. Alternatively, users can use D2D to get the media content from nearby user terminals that have obtained media services. In this way, the downlink transmission pressure of operator cellular networks can be eased. Moreover, the cellular communication between short-distance users can be switched to the D2D mode to offload cellular traffic.
Emergency Communication
When natural disasters such as earthquakes occur, traditional communication network infrastructure can get damaged and the network may even collapse. This greatly hampers rescue efforts. This problem can be solved by introducing D2D communication. Although the communication network infrastructure may be damaged, a wireless network can still be set up between terminals based on the D2D connection. This means that an ad hoc network can be established based on multi-hop D2D to ensure smooth wireless communication between terminals. A wireless network affected by terrain or buildings may have blind spots. With single-hop or multi-hop D2D communication, users in the blind spots can be connected to user terminals that are in coverage areas and then be connected to the wireless network.
IoT Enhancement
One of the goals of developing mobile communication is to establish an extensive interconnected network that contains various types of terminals. This is also one of the starting points for developing the Internet of Things (IoT) in the cellular communication framework. The industry forecasts that by 2020 there will be 50 billion cellular access terminals on a global scale and most of them will be machine terminals with the IoT feature. If D2D is combined with IoT, a truly interconnected wireless network will be created.
A typical application of D2D-based IoT enhancement is vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication in the Internet of Vehicles (IoV). When running at high speeds, a vehicle can warn nearby vehicles in D2D mode before it changes lanes or slows down (Fig. 2). According to the received warnings, nearby vehicles alert drivers or even automatically control the driving in an emergency situation so that drivers can react more quickly to reduce the number of traffic accidents. Furthermore, using D2D discovery technology, vehicles can reliably detect and identify specific vehicles nearby, such as those vehicles that may cause danger at intersections and those specific vehicles (school buses or vehicles carrying dangerous goods) that need special attention.
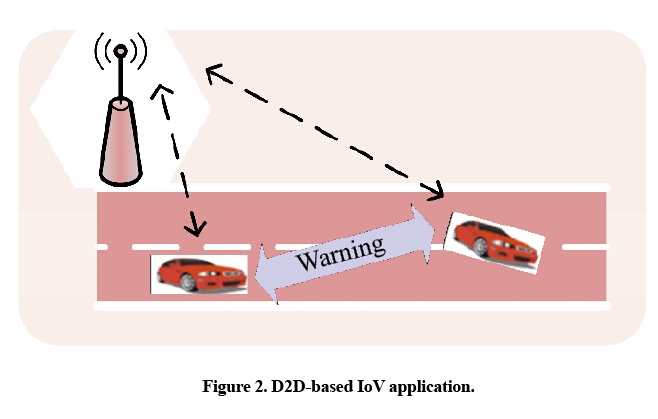
Based on the communication delay and neighbor discovery features, D2D communication has inherent advantages when being applied for IoV security.
Because there are many IoT terminals in a 5G network, access load has become a serious issue. However, D2D-based network access is expected to solve this problem. In a scenario where there are many terminals, low-cost terminals can access nearby special terminals in D2D mode instead of being directly connected to base stations. Through these special terminals, connections to the cellular network are established. If multiple special terminals are isolated in space, the wireless resources for access to low-cost terminals can be reused by these special terminals. This not only relieves access pressure on base stations but also improves spectrum efficiency. Furthermore, compared with small cell structure in the existing 4G networks, the D2D-based access mode is more flexible and costs less.
In a smart home application, a smart terminal can be used as a special terminal. Wireless appliances in the smart home access the smart terminal in D2D mode, and the smart terminal can access the base station in a traditional cellular mode. The cellular-based D2D communication may make a real breakthrough for the development of the smart home industry.
Other Applications
5G D2D can also be applied in other potential scenarios, such as multiuser MIMO enhancement, cooperative relaying, and virtual MIMO. In the traditional multiuser MIMO, base stations determine pre-coding weights based on respective channel feedback of terminals to create nulls and eliminate interference between users. After D2D is introduced, paired users can directly exchange information about channel status. In this way, terminals can feed the joint channel status information to base stations and improve the performance of multi-user MIMO.
D2D can also help to solve problems in new wireless communication scenarios. In the indoor positioning, terminals cannot obtain satellite signals when they are indoors. In this case the traditional satellite-based positioning does not work. However, in the D2D-based indoor positioning, pre-deployed terminals with given location information or common outdoor terminals with given position can determine the location of terminals to be positioned, and support indoor positioning in 5G networks at a low cost.
Key 5G D2D Techniques
In the above applications, potential 5G D2D techniques at the access side include:
● D2D discovery. This involves detecting and identifying nearby D2D terminals. For multi-hop D2D networks, this technique should be considered in combination with routing and to meet the needs of special 5G scenarios such as efficient discovery in ultra-dense networks and ultra-low latency in IoV scenarios.
● D2D synchronization. Certain scenarios such as outdoor coverage or multi-hop D2D networks may present a big challenge to system synchronization.
● wireless resource management. 5G D2D communication may include broadcast, multicast, and unicast, and can be used in multi-hop and relay scenarios. Therefore, radio resource management and scheduling in 5G networks is more different and complex than in traditional cellular networks.
● power control and interference coordination. Cellular-based D2D has the advantage of controllable interference over traditional peer-to-peer (P2P). However, cellular-based D2D creates extra interference in cellular communication. Moreover, considering multi-hop and unauthorized LTE-U spectrum as well as high-frequency communication in 5G D2D, research into power control and interference coordination will be critical.
● communication mode switching. It includes the switching between D2D and cellular modes, between cellular D2D and other P2P (such as WLAN) modes, and between authorized spectrum D2D and LTE-U D2D modes. Advanced communication mode switching can maximize the performance of wireless communication systems.