China Mobile: Building a Future-Proof RCS Network
Tencent, Alibaba and NetEase have invested heavily in WeChat, Laiwang and Credulity respectively, in order to preempt internet communication. SMS is being overshadowed by emerging OTT services. People used to send or receive text messages; now they use rich-text messages that include voice and video. Communication trends have changed. Li Yue, president of China Mobile, released a white paper China Mobile: Next-Generation Converged Communications at the GTI Summit at GSMA Mobile World Congress 2014. This white paper aims to redefine basic communication services, which should provide superior experience in the 4G era. The paper explains that the core component is rich communication services (RCS), which is a service-capability suite planned by GSMA that enhances calls, messaging, and phonebook.
RCS is based on existing communication capabilities, but will converge voice, messaging, video, presence, community networks, and other means of communication and provide users with a more diverse communication experience.
In October 2014, China Mobile chose ZTE as the exclusive contractor to construct the IP multimedia subsystem (IMS) RCS network.
World’s Largest Commercial IMS-based RCS Network
As originally planned by China Mobile, the capacity of their RCS network in phase one is more than 100 million users, 16 million of whom will be able to use the network simultaneously. The RCS network is China Mobile’s largest network and also the world’s largest commercial IMS-based RCS network.
China Mobile gave full consideration to RCS features and designed the network accordingly. The home subscriber server (HSS) provides storage and fast processing of mass user data. The call-session control function (CSCF) enables intelligent service load sharing. The serving-call session-control function uses policies that encompass message type, application server keep-alive status, user service subscription information, and terminal service capabilities to automatically distribute massive amounts of service traffic to appropriate service NEs.
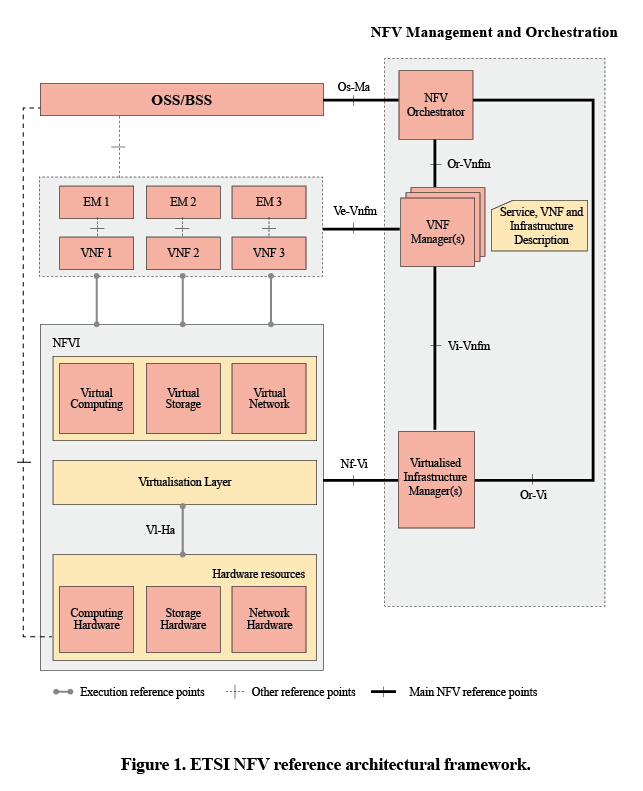
World’s First Virtualized Commercial RCS Network Based on Standard ETSI NFV Architecture
China Mobile has used ZTE’s virtualization technology to cope with rapid service growth, to deploy their RCS network rapidly, and to reduce network maintenance costs. This technology is based on the ETSI NFV architecture (Fig. 1). China Mobile’s RCS network is the world’s first virtualized commercial RCS network based on the ETSI NFV architecture.
Any Access, Any UE, Anytime
To enable future communication between various devices, when designing the RCS network, China Mobile used the IMS architecture, defined by 3GPP, and RCS version 5.1, defined by GSMA. All the terminals, 3GPP-compliant or GSMA-compliant, can access the China Mobile RCS network. Smart access and auto-configuration are also included in the China Mobile RCS network. These enable flexible policy control so that different terminals can access the RCS network at different times and by different means.
Smart access and auto configuration are implemented as follows. Before a terminal accesses a service, the terminal connects the device-management server (DMS) in the RCS network. The DMS checks the terminal app type (web or native), terminal access mode (WLAN, 2G, 3G or 4G), terminal IP address, and request time and then generates a configuration file. This file, which includes address information of various RCS servers and terminal user ID, is sent to the terminal in HTTPS mode.
Policies are set on session border controllers to provide various means of access. Users in an office can access the RCS network through firewalls of their business. The SBC supports business firewall traversal through tunnels. A home user can access the RCS network through a WLAN. The SBC supports transport layer security connections to ensure information is transmitted securely. An outdoor user can access the RCS network through a 2G, 3G or LTE network. The SBC supports TCP connections to ensure proper service operation and reduce terminal battery consumption.
Varied Services
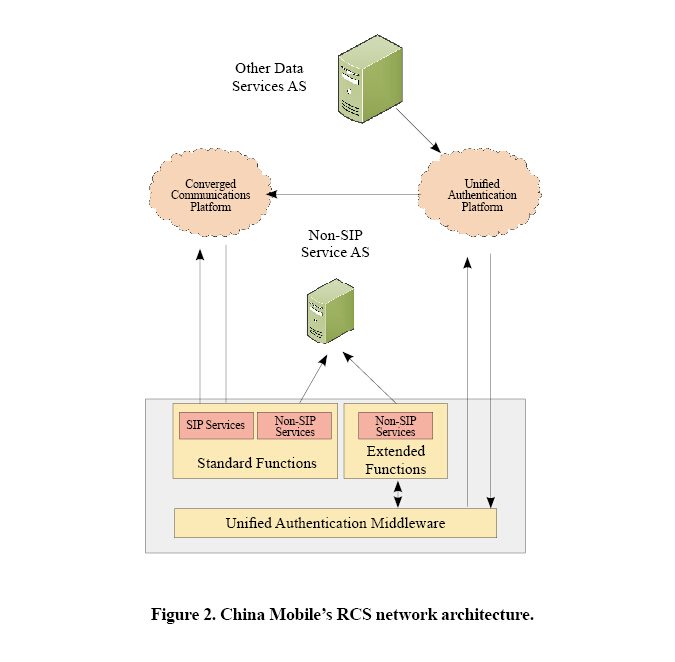
China Mobile’s RCS network (Fig. 2) provides varied services, including one-key multicall services and automatic certification. The former are based on enhanced phonebook. China Mobile’s RCS network not only has the basic functions of an existing telecom services but also new functions of the internet. The RCS network allows a user to perform various operations based on the phonebook. You can press a key to make a multi-party call and select multiple contacts from the phonebook to join the call. During the call, you can add new members or remove existing ones. On the screen, you can also observe the number of members in real time. This greatly increases the availability of existing service functions.
China Mobile’s RCS network uses a unified certification solution to allow a user to automatically and directly access RCS services after installing a USIM card. The user does not have to enter their user name or password. The unified certification solution enables multiple service NEs to share the same authentication data.
When a terminal is powered on for the first time and a native app is started, or a mobile app is started for the first time, the DMS in the network determines that the RCS function is not enabled on the terminal. The DMS interacts with unified certification platform deployed in a centralized manner and generates RCS app password for the terminal. The HSS, AS, and ENUM/DNS are involved in RCS account creation. The DMS pushes the app password to the HSS in the RCS network, and after the account has been created, the DMS sends the generated private user identity (PVI) and public user identity (PUI) to the terminal.
After receiving the configuration information, the terminal invokes the embedded unified certification middleware to interact with the unified certification platform. In this way, the terminal obtains the app password generated during account creation and starts the registration flow in the RCS network.
The S-CSCF obtains the corresponding authentication data, including the app password generated during account creation from the HSS. Because all application passwords are generated by the unified certification platform and all password data is the same, the authentication is passed, and the terminal logs in to the RCS network. The user of the terminal is not aware of this process.
This unified certification solution greatly simplifies user operation and improves user experience in a secure manner.
In December 2014, China Mobile’s RCS network was demonstrated before 5000 people at the China Mobile Global Partner Conference. Services were interworked between terminals of different manufacturers. This was an important milestone for converged communication of China Mobile and laid a solid foundation for RCS commercialization.