Focusing on User Experience to Build Converged, Innovative 5G Networks

About 5G
In today’s ICT industry, physical network elements are continually evolving and merging with each other. Greater consideration of user experience represents an advance in smart terminals and network technologies in the mobile ICT industry. 5G will provide much better user experience and makes further convergence and innovation possible in terms of terminals, wireless network and services. 5G will revolutionize information perception, acquisition, participation, and control. 5G services will expand to include more enterprise users. A 5G network will leverage the excellent features of a LAN and cellular network; it will become smarter and friendlier and serve a broader range of purposes. It will penetrate all aspects of life and coexist with other successful technologies.
Challenges
5G does not only imply increased bandwidth and meeting the needs of personal users; it also implies a greater focus on user experience and meeting the needs of internet-connected social applications. In achieving these ends, there are three big challenges: providing ubiquitous services, handling massive data connections, and ensuring energy efficiency.
Ubiquitous Services
In the M-ICT era, services will be everywhere. People will require more efficient mobile offices, information sharing, social interaction, e-commerce, internet finance, and other mobile internet services. R&D on 5G will begin with improving user experience and will shift to setting up a user perception model based on meeting service needs. Then, the R&D focus will shift to improving key technical indicators, such as network capacity, bandwidth guarantee, peak rate, network delay, and high-precision indoor positioning.
Massive Data Connections
A 5G network establishes high-speed person-to-person, person-to-machine, and machine-to-machine connections. With information as the link between the physical and digital worlds, a ubiquitous, general-purpose, high-speed interconnected network needs to be built up. 5G provides efficient connections for social life and enterprise applications. These connections are massive and will be a big challenge in terms of network capacity and robustness. Therefore, 5G has to incorporate into the mobile internet industry all the value links and production elements associated with the office, shopping, medical care, education, entertainment, transport, and social life. A physical map is thus set up on the internet, and the physical world is integrated with the digital world.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is essential in 5G. In the M-ICT era, a big, dense 5G networks with ubiquitous services and massive data connections will consume a huge amount of energy if built with available technologies. Terminals connect man and machine to the entire network and directly affect what the user experiences. There will be many power-related challenges in developing 5G terminals that incorporate all kinds of sensing and new media technologies, materials, and entertainment facilities. It is therefore necessary to change network architecture and restructure NEs and related functions in order to save energy on both the network and terminal side.
Technological Expectations
5G R&D will center on enhancing user experience, orienting applications to the information society, and building an integrated smart network.
Technologies for Super-Heavy Data Traffic
Smart mobile terminals and cloud applications will fuel the explosive growth of data traffic. To support super-heavy data traffic, greater research needs to be done on wireless radio link, spectrum utilization, and networking (Fig. 1).
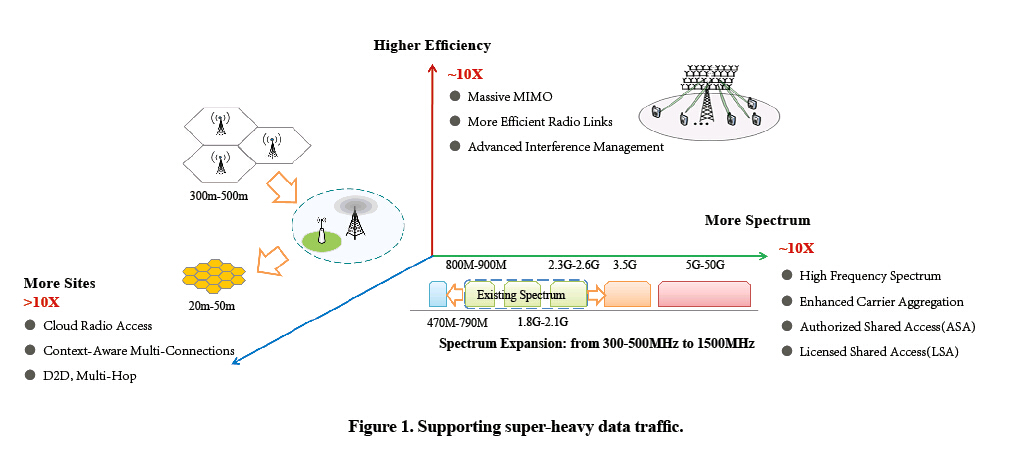
Radio links can be made more efficient in terms of coding and modulation, multiple access technology, and receivers. Nonlinear multiuser pre-coding, new joint coding and modulation, and network coding can all be explored. Multiple access technology includes non-orthogonal multiple access technology. In terms of receivers, much research has been done on 1) new waveforms that support MIMO and 2) full duplex short radio links. Combining all of these technologies can significantly improve transmission in a wireless network.
5G provides higher bandwidth by adding new operating spectrum that includes frequencies above 3 GHz or even some sub-millimeter wavelengths. These frequencies provide indoor and hotspot data rates similar to that possible with optical fiber level. With these new frequencies, 5G can enable dynamic, intelligent spectrum management so that the network operates on unauthorized or unassigned frequencies.
5G will be important for local hotspots with super-heavy date traffic. Bandwidth capacity per unit space can be improved through dense networking. Combinations of various new high-speed wireless LAN access points and small cells can be densely deployed to form a network with super-high bandwidth capacity.
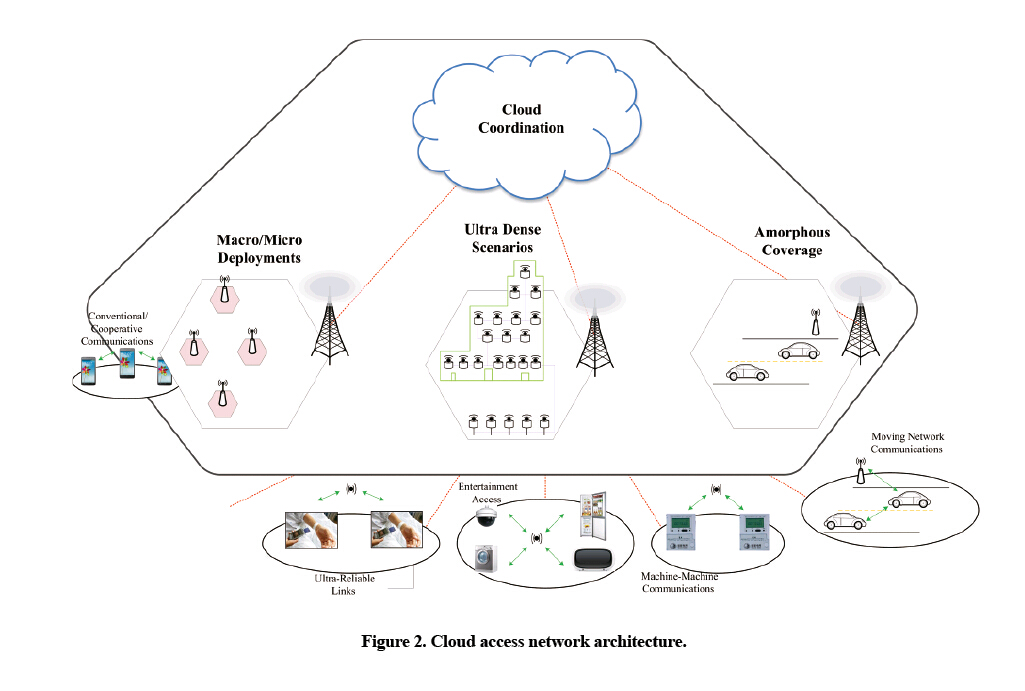
Intelligent Cloud Networking
5G network architecture needs to be adaptable to fluctuation in data traffic, and this means the network needs to be intelligent and cloud-based. Person-to-person, person-to-machine, and machine-to-machine connections will all need to be seamless. Any individual, enterprise, or even machine could be the consumer or provider of information services. They form a new relational digital ecosystem and drive the rapid growth of data traffic. An intelligent cloud network must be able to cope with related challenges.