Big Data Service Models
● Large-scale investment but uncertain outcome. Most big data applications have low cost performance.
● The gains of big data applications are limited, because operators can provide only a few types of data subject to technical, political and legal restrictions.
● Operators are pipelined and marginalized in the emerging big data chain.
To overcome these challenges, the key is to find an applicable big data service model that converts potential value into benefits. The following will brief on four big data service models that can be adopted.
Internal Application Model
● Customer experience-oriented network planning, maintenance, and optimization.
● Telecom service-oriented precise marketing.
For example, Orange applies big data to enhance user experience. The internal application model is the basis for operators to carry out big data operations designed for external markets. It can help operators optimize operations, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
Data Sales Model
The data sales model, namely, external cooperation, is a model where operators sell data products or services, which are formed by the valuable data of operators, to make profits. The sold data products or services may be consultation reports, traffic inquiries, advertising services, and credit services.
Because operators can collect only a few types of data, the value generated is limited for a third party. The income from a single service is so small that huge investments in platform construction do not provide adequate return. Therefore, to benefit from the data sales model, operators must have a professional team to delve in-depth on the data and associate it with external industry data to enhance the data value. Generally, to ensure scalability and safety, response speed, and service development, one unit will be responsible for unified and intensive management. This can save construction costs and improve efficiency.
For instance, Dynamic Insights, a specialized department of Telefónica, operates global data assets. Its SmartStep service, after collecting and analyzing users’ location information, delivers location-based services for transportation and retail industries. A typical case is Morrisons, the UK’s fourth largest food retailer. The SmartStep service, by analyzing historical tracks of people in different areas, instructed Morrisons to deliver coupons to areas where repeat customers can be caught with the highest speed at the lowest costs. By partnering with Dynamic Insights, Morrisons saw a 150 percent increase in the number of new customers and repeat customers.
Most operators participate in smart city construction and are involved in industries such as digital home, intelligent car, healthcare, tourism, and education. If operators become involved in service operation by establishing an industry operating platform based on big data, collect service-related data and combine it with telecom data, and provide data to industry services, they can increase the value of data and generate more revenue.
Take smart tourism as an example. Travel agencies can obtain historical data about tourists and target customers’ classification information from operators, and combine it with their own historical order data to find out potential customers and recommend destinations and products to them. On the one hand, travel agencies can store historical order data to the big data tourism platform and associate it with location and user classification data provided by operators. On the other hand, operators can get revenue from travel agencies for data usage and share the data association result, which enrich destination selection and product preference data.
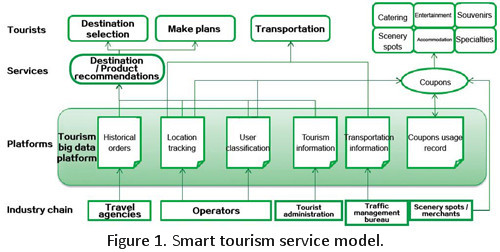
Operators can also cooperate with merchants to provide tourism product coupons to target customers, associate the coupon usage with location and user classification data in order to understand their consumption habits to certain tourism products, increasing recommendation accuracy and further increase revenue.
Smart tourism helps operators integrate various kinds of tourism-related data, including public government information, merchandise catalogue, consumption records, trips, and internet public opinions on the big data tourism platform. These data are associated and add value to each other, bringing more profits for all participants in the tourism industry chain.
Data Operating Model
By operating the big data platform, operators can raise their status in the big data industry chain and generate new revenue, such as data storage and computing rent, data transaction fees, and revenue from monetization of data. What’s more, operators can obtain data from other industries by sharing the big data exchange platform and through data transactions, so as to serve their self-owned services, and create innovative services.
China’s national big data strategy creates opportunities for the data operating model. With the development of big data applications in various industries, big data infrastructure, especially common big data platforms are required. Operators have high social credibility and strong technical and operating capabilities, which enable them to become big data operators.
Summary
In most cases, the preceding four models coexist and support each other.
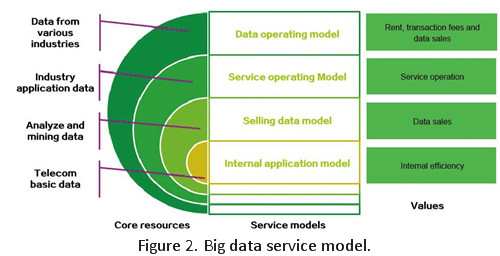
The internal application model is the basis of big data operation. In at least one or two years, it will still be the main revenue source for big data services. Data acquisition, processing, and analysis will apply mainly to the internal application model. However, with in-depth optimization, the marginal revenues from this model decrease gradually.
Revenues from the other three models rise as data requirements from the external environment increase, so they become the future revenue growth points. Moreover, the three external models help operators obtain data from other industries and increase data value.
The data sales model is clear and generates profits quickly, so it is widely used by operators. However, the costs in this model are quite high, and small-scale operating services cannot make a profit.
The service operating model has been adopted in the wave of smart city and internet+ construction. By operating the industry big data platform, operators can monetize service-based data and promote intelligent operation as well.
The data operating model enables telecom operators to transit to big data operators, integrating data from various industries, raising status in the industry chain, and creating new values.