Building a VAS Dream Factory
Mobile value-added services (VAS) have developed rapidly in recent years, and with fast market penetration, have brought huge economic benefits to Chinese operators. A new mobile information service industry has come into being, comprising infrastructure telecom operators, service providers (SPs), content providers (CPs), and a variety of application providers (APs). A primary concern of operators is to further strengthen and expand their VAS businesses.
Unified Service Platform
With the rapid growth of ICT and the Internet, demand for integrated, multimedia, and personalized mobile VAS has grown significantly. As a result, enhanced service capability has become the objective in research and application of new network technologies. The key to achieving this objective is service convergence or a mobile VAS platform. Deploying services rapidly to meet market demands has therefore become a core competitive strategy, and service development a key part of network operation.
As service development increases in line with terminal, network, and software evolution, an urgent need arises for an open and converged service environment based on existing service development and provisioning systems of Internet and telecom networks. A new service environment geared for the future will provide next generation tools for simple and easy service development so that APs, SPs, and CPs—as well as clients and subscribers—can co-operate in the rapid creation of new services.
Open Deployment Environment
Operators urgently need a “service hatchery” that can constantly roll out new services. Modules could simply be expanded on a Unified Open Environment (UOE) without the need for a new platform. This facilitates interoperability between application platforms, and helps operators reduce TCO and hasten the deployment of services to end users.
China Mobile has a clear track record in VAS operation. Initially, China Mobile knew little about operating VAS nor the services that would be profitable. A large number of SPs were introduced to deploy a variety of services; but inevitably, China Mobile became a mere “pipe” provider. Profit-motivations at this stage meant that many SPs engaged in behavior that was counterproductive to China Mobile. To remedy this problem, China Mobile set up a series of management platforms to regulate SP behavior in the second stage. Although SPs were required to deploy their VAS on a unified platform, fraudulent behavior involving consumption of services by SPs themselves could not be completely avoided. To build a healthy industrial chain, China Mobile started to weaken the role of SPs, and in the third stage, gradually turned them into CPs. The operator would provide certain high revenue services with strong user loyalty on their own. A self-operated service platform was therefore necessary for successful VAS operation. By integrating an operator’s internal resources with social resources, and adopting unified policy and user interface, a self-operated service platform can offers feature-rich and personalized value-added services.
Responding to these needs, ZTE has launched a self-operated service platform that helps operators establish a unified, open, and orderly VAS system.
Self-Operated Service Platform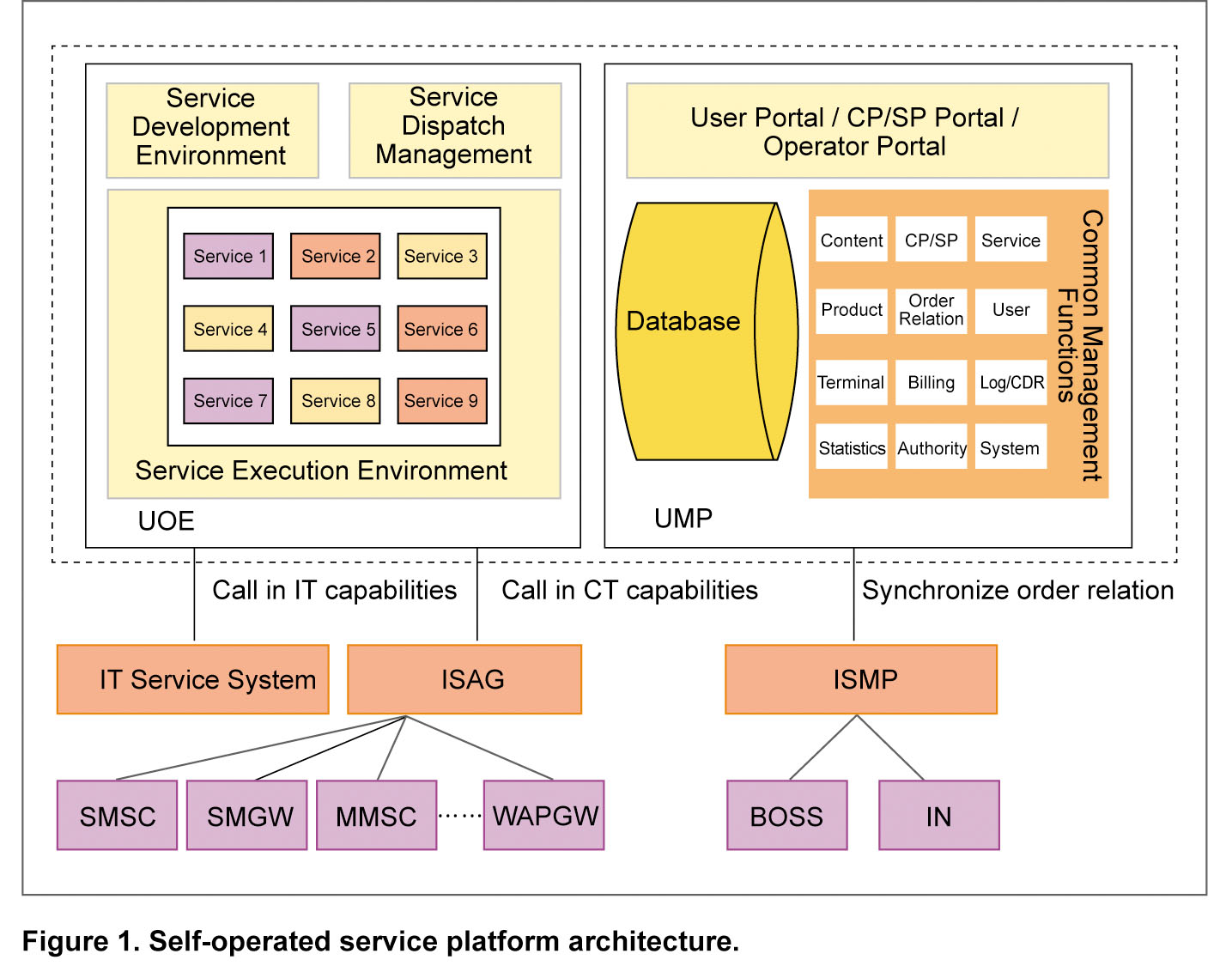
Functional modules
A self-operated service platform consists of UOE and Unified Management Platform (UMP). UOE is responsible for openness and adapting different capabilities, and provides a stable application-managed environment. Its downstream network elements are engines for the various capabilities. UMP is responsible for man-machine interaction, maintenance of management data, and service authentication and rating.
■ Service access
The service access system calls in various service capabilities to be registered. The platform divides these registered capabilities into two categories: capability requests initiated by the system to the outside, and capability requests the system receives from the outside. The former also called atomic services (such as sending SMS/MMS, and checking weather forecast), and the latter uplink service (such as SMS/MMS uplink requests). These capabilities can be registered, upgraded, or cancelled, which makes the system scalable and flexible.
■ Service development environment
UOE provides three tools for users and service developers: a programmable development tool for people with programming ability; a graphic wizard development tool for people with no programming ability but good VAS business and computer literacy; and a web-based service development tool for people who have no technical background but are familiar with VAS business.
■ Service execution environment
Services are created in the development environment and deployed in the service execution environment. The execution environment is a safe, reliable, stable, and high-performance container that provides engine, management, and basic functions.
■ Service test environment
Service test environment includes network and terminal simulation. One network simulation environment supports multiple simulated terminals, and all Integrated Service Access Gateway (ISAG) services can be simulated on the terminals.
■ Service management
Service management involves service lifecycle and status management as well as service simulation and monitoring.
Value chain
A self-operated service platform that supports fast service development and deployment gives wings to new service ideas and helps operators increase profit. Through a unified and open environment, all network capabilities can be converged and opened. UMP can be used to manage these capabilities and to support interaction with external IT systems. A self-operated platform has the following advantages:
■ Multiple service support;
■ Fast service deployment;
■ Controllable service testing;
■ Fast service access.
With a self-operated platform, network resources can be converged. Service discovery, verification, execution, and billing can also be converged, and this gives VAS its core competitive advantage. Content provided by CPs is launched and deployed in UOE, authenticated and charged by UMP, and finally used by subscribers. The operator becomes a bridge connecting CPs and subscribers, and a stable revenue stream can be created. A self-operated service platform helps an operator build a VAS dream factory.